Pharmacokinetic properties of 2nd-generation fibroblast growth factor-1 mutants for therapeutic application
- PMID: 23133616
- PMCID: PMC3486806
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0048210
Pharmacokinetic properties of 2nd-generation fibroblast growth factor-1 mutants for therapeutic application
Abstract
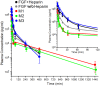
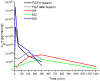
Fibroblast growth factor-1 (FGF-1) is an angiogenic factor with therapeutic potential for the treatment of ischemic disease. FGF-1 has low intrinsic thermostability and is characteristically formulated with heparin as a stabilizing agent. Heparin, however, adds a number of undesirable properties that negatively impact safety and cost. Mutations that increase the thermostability of FGF-1 may obviate the need for heparin in formulation and may prove to be useful "2nd-generation" forms for therapeutic use. We report a pharmacokinetic (PK) study in rabbits of human FGF-1 in the presence and absence of heparin, as well as three mutant forms having differential effects upon thermostability, buried reactive thiols, and heparin affinity. The results support the hypothesis that heparan sulfate proteoglycan (HSPG) in the vasculature of liver, kidney and spleen serves as the principle peripheral compartment in the distribution kinetics. The addition of heparin to FGF-1 is shown to increase endocrine-like properties of distribution. Mutant forms of FGF-1 that enhance thermostability or eliminate buried reactive thiols demonstrate a shorter distribution half-life, a longer elimination half-life, and a longer mean residence time (MRT) in comparison to wild-type FGF-1. The results show how such mutations can produce useful 2nd-generation forms with tailored PK profiles for specific therapeutic application.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures






References
-
- Levi-Montalcini R (1964) The Nerve Growth Factor. Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences 118: 149–170. - PubMed
-
- Hoober JK, Cohen S (1967) Epidermal growth factor. 1. The stimulation of protein and ribonucleic acid synthesis in chick embryo epidermis. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta 138: 347–356. - PubMed
-
- Schenkein I, Levy M, Bueker ED, Tokarsky E (1968) Nerve growth factor of very high yield and specific activity. Science 159: 640–643. - PubMed
-
- Schumacher B, Stegmann T, Pecher P (1998) The stimulation of neoangiogenesis in the ischemic human heart by the growth factor FGF: first clinical results. J Cardiovasc Surg (Torino) 39: 783–789. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

