The Arabidopsis thaliana immunophilin ROF1 directly interacts with PI(3)P and PI(3,5)P2 and affects germination under osmotic stress
- PMID: 23133621
- PMCID: PMC3487907
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0048241
The Arabidopsis thaliana immunophilin ROF1 directly interacts with PI(3)P and PI(3,5)P2 and affects germination under osmotic stress
Abstract
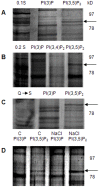
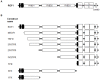
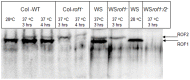
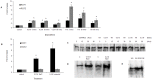
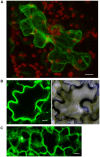
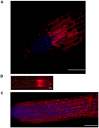
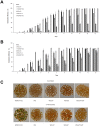
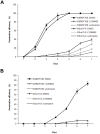
A direct interaction of the Arabidopsis thaliana immunophilin ROF1 with phosphatidylinositol-3-phosphate and phosphatidylinositol-3,5-bisphosphate was identified using a phosphatidylinositol-phosphate affinity chromatography of cell suspension extracts, combined with a mass spectrometry (nano LC ESI-MS/MS) analysis. The first FK506 binding domain was shown sufficient to bind to both phosphatidylinositol-phosphate stereoisomers. GFP-tagged ROF1 under the control of a 35S promoter was localised in the cytoplasm and the cell periphery of Nicotiana tabacum leaf explants. Immunofluorescence microscopy of Arabidopsis thaliana root tips verified its cytoplasmic localization and membrane association and showed ROF1 localization in the elongation zone which was expanded to the meristematic zone in plants grown on high salt media. Endogenous ROF1 was shown to accumulate in response to high salt treatment in Arabidopsis thaliana young leaves as well as in seedlings germinated on high salt media (0.15 and 0.2 M NaCl) at both an mRNA and protein level. Plants over-expressing ROF1, (WSROF1OE), exhibited enhanced germination under salinity stress which was significantly reduced in the rof1(-) knock out mutants and abolished in the double mutants of ROF1 and of its interacting homologue ROF2 (WSrof1(-)/2(-)). Our results show that ROF1 plays an important role in the osmotic/salt stress responses of germinating Arabidopsis thaliana seedlings and suggest its involvement in salinity stress responses through a phosphatidylinositol-phosphate related protein quality control pathway.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

Similar articles
-
Differential isolation and identification of PI(3)P and PI(3,5)P2 binding proteins from Arabidopsis thaliana using an agarose-phosphatidylinositol-phosphate affinity chromatography.J Proteomics. 2013 Oct 8;91:580-94. doi: 10.1016/j.jprot.2013.08.020. Epub 2013 Sep 2. J Proteomics. 2013. PMID: 24007659
-
Arabidopsis immunophilins ROF1 (AtFKBP62) and ROF2 (AtFKBP65) exhibit tissue specificity, are heat-stress induced, and bind HSP90.Plant Mol Biol. 2007 Jan;63(2):237-55. doi: 10.1007/s11103-006-9085-z. Epub 2006 Nov 2. Plant Mol Biol. 2007. PMID: 17080288
-
Arabidopsis ROF1 (FKBP62) modulates thermotolerance by interacting with HSP90.1 and affecting the accumulation of HsfA2-regulated sHSPs.Plant J. 2009 Aug;59(3):387-99. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-313X.2009.03878.x. Epub 2009 Apr 2. Plant J. 2009. PMID: 19366428
-
Selective autophagy regulates heat stress memory in Arabidopsis by NBR1-mediated targeting of HSP90.1 and ROF1.Autophagy. 2021 Sep;17(9):2184-2199. doi: 10.1080/15548627.2020.1820778. Epub 2020 Sep 24. Autophagy. 2021. PMID: 32967551 Free PMC article.
-
Involvement of Arabidopsis ROF2 (FKBP65) in thermotolerance.Plant Mol Biol. 2010 Jan;72(1-2):191-203. doi: 10.1007/s11103-009-9561-3. Epub 2009 Oct 29. Plant Mol Biol. 2010. PMID: 19876748
Cited by
-
Proteome Analysis of the ROF-FKBP Mutants Reveals Functional Relations among Heat Stress Responses, Plant Development, and Protein Quality Control during Heat Acclimation in Arabidopsis thaliana.ACS Omega. 2023 Dec 26;9(2):2391-2408. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.3c06773. eCollection 2024 Jan 16. ACS Omega. 2023. PMID: 38250364 Free PMC article.
-
The chromatin remodeler ZmCHB101 impacts alternative splicing contexts in response to osmotic stress.Plant Cell Rep. 2019 Feb;38(2):131-145. doi: 10.1007/s00299-018-2354-x. Epub 2018 Nov 15. Plant Cell Rep. 2019. PMID: 30443733
-
Phospholipids in Salt Stress Response.Plants (Basel). 2021 Oct 17;10(10):2204. doi: 10.3390/plants10102204. Plants (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34686013 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Diverse Physiological Functions of FAB1 and Phosphatidylinositol 3,5-Bisphosphate in Plants.Front Plant Sci. 2019 Mar 22;10:274. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2019.00274. eCollection 2019. Front Plant Sci. 2019. PMID: 30967882 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Involvement of Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase in the regulation of proline catabolism in Arabidopsis thaliana.Front Plant Sci. 2015 Jan 12;5:772. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2014.00772. eCollection 2014. Front Plant Sci. 2015. PMID: 25628629 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Di Paolo G, De Camilli P (2006) Phosphoinositides in cell regulation and membrane dynamics. Nature 443: 651–657. - PubMed
-
- Behnia R, Munro S (2005) Organelle identity and the signposts for membrane traffic. Nature 438: 597–604. - PubMed
-
- Balla T (2005) Inositol-lipid binding motifs: signal integrators through protein lipid and protein-protein interactions. J Cell Sci 118: 2093–2104. - PubMed
-
- Cooke FT, Dove SK, McEwen RK, Painter G, Holmes AB, et al. (1998) The stress activated phosphatidylinositol 3-phosphate 5-kinase Fab1p is essential for vacuole function in S. cerevisiae. Curr Biol 8: 1219–1222. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

