Multiple gamma knife radiosurgery for multiple metachronous brain metastases associated with lung cancer : survival time
- PMID: 23133721
- PMCID: PMC3488641
- DOI: 10.3340/jkns.2012.52.4.334
Multiple gamma knife radiosurgery for multiple metachronous brain metastases associated with lung cancer : survival time
Abstract
Objective: We compared the survival time between patients with multiple gamma knife radiosurgery (GKRS) and patients with a single GKRS plus whole brain radiation therapy (WBRT), in patients with multiple metachronous brain metastases from lung cancer.
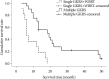
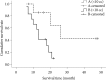
Methods: From May 2006 to July 2010, we analyzed 31 patients out of 112 patients who showed multiple metachronous brain metastases. 20 out of 31 patients underwent multiple GKRS (group A) and 11 patients underwent a single GKRS plus WBRT (group B). We compared the survival time between group A and B. Kaplan-Meier method and Cox proportional hazards were used to analyze relationship between survival and 1) the number of lesions in each patient, 2) the average volume of lesions in each patient, 3) the number of repeated GKRS, and 4) the interval of development of new lesions, respectively.
Results: Median survival time was 18 months (range 6-50 months) in group A and 6 months (range 3-18 months) in group B. Only the average volume of individual lesion (over 10 cc) was negatively related with survival time according to Kaplan-Meier method. Cox-proportional hazard ratio of each variable was 1.1559 for the number of lesions, 1.0005 for the average volume of lesions, 0.0894 for the numbers of repeated GKRS, and 0.5970 for the interval of development of new lesions.
Conclusion: This study showed extended survival time in group A compared with group B. Our result supports that multiple GKRS is of value in extending the survival time in patients with multiple metachronous brain metastases, and that the number of the lesions and the frequency of development of new lesions are not an obstacle in treating patients with GKRS.
Keywords: Gamma knife radiosurgery; Lung cancer; Metastases; Survival time; Whole brain radiation therapy.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Gamma Knife radiosurgery for brain metastases from pulmonary large cell neuroendocrine carcinoma: a Japanese multi-institutional cooperative study (JLGK1401).J Neurosurg. 2016 Dec;125(Suppl 1):11-17. doi: 10.3171/2016.7.GKS161459. J Neurosurg. 2016. PMID: 27903179
-
Clinical outcomes in patients with brain metastases from breast cancer treated with single-session radiosurgery or whole brain radiotherapy.J Neurosurg. 2016 Dec;125(Suppl 1):26-30. doi: 10.3171/2016.7.GKS161541. J Neurosurg. 2016. PMID: 27903186
-
Clinical outcome in gamma knife radiosurgery for metastatic brain tumors from the primary breast cancer : prognostic factors in local treatment failure and survival.J Korean Neurosurg Soc. 2013 Oct;54(4):329-35. doi: 10.3340/jkns.2013.54.4.329. Epub 2013 Oct 31. J Korean Neurosurg Soc. 2013. PMID: 24294457 Free PMC article.
-
A Single-Institution Analysis of 126 Patients Treated with Stereotactic Radiosurgery for Brain Metastases.Front Oncol. 2017 May 12;7:90. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2017.00090. eCollection 2017. Front Oncol. 2017. PMID: 28553615 Free PMC article.
-
Gamma Knife Radiosurgery for the Treatment of Trigeminal Neuralgia in Patients with Multiple Sclerosis: A Single-Center Retrospective Study and Literature Review.World Neurosurg. 2021 May;149:e92-e100. doi: 10.1016/j.wneu.2021.02.074. Epub 2021 Feb 25. World Neurosurg. 2021. PMID: 33640527 Review.
Cited by
-
Stereotactic Radiosurgery of Multiple Brain Metastases: A Review of Treatment Techniques.Cancers (Basel). 2023 Nov 14;15(22):5404. doi: 10.3390/cancers15225404. Cancers (Basel). 2023. PMID: 38001664 Free PMC article. Review.
-
[Advances in treatment of brain metastases from primary non-small cell lung cancer].Zhongguo Fei Ai Za Zhi. 2014 Dec;17(12):877-83. doi: 10.3779/j.issn.1009-3419.2014.12.10. Zhongguo Fei Ai Za Zhi. 2014. PMID: 25539615 Free PMC article. Review. Chinese.
-
Effects of an Epithelial Growth Factor Receptor-Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitor Add-on in Stereotactic Radiosurgery for Brain Metastases Originating from Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer.J Korean Neurosurg Soc. 2015 Sep;58(3):205-10. doi: 10.3340/jkns.2015.58.3.205. Epub 2015 Sep 30. J Korean Neurosurg Soc. 2015. PMID: 26539262 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Aoyama H, Shirato H, Tago M, Nakagawa K, Toyoda T, Hatano K, et al. Stereotactic radiosurgery plus whole-brain radiation therapy vs stereotactic radiosurgery alone for treatment of brain metastases : a randomized controlled trial. JAMA. 2006;295:2483–2491. - PubMed
-
- Aoyama H, Tago M, Kato N, Toyoda T, Kenjyo M, Hirota S, et al. Neurocognitive function of patients with brain metastasis who received either whole brain radiotherapy plus stereotactic radiosurgery or radiosurgery alone. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2007;68:1388–1395. - PubMed
-
- Auchter RM, Lamond JP, Alexander E, Buatti JM, Chappell R, Friedman WA, et al. A multiinstitutional outcome and prognostic factor analysis of radiosurgery for resectable single brain metastasis. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 1996;35:27–35. - PubMed
-
- Bahl A, Kumar M, Sharma DN, Jothy Basu, KS, Jaura MS, Rath GK, et al. Reirradiation for progressive brain metastases. J Cancer Res Ther. 2009;5:161–164. - PubMed
-
- Bhatnagar AK, Flickinger JC, Kondziolka D, Lunsford LD. Stereotactic radiosurgery for four or more intracranial metastases. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2006;64:898–903. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

