Synthesis, radiolabelling and in vitro and in vivo evaluation of a novel fluorinated ABP688 derivative for the PET imaging of metabotropic glutamate receptor subtype 5
- PMID: 23133799
- PMCID: PMC3478118
Synthesis, radiolabelling and in vitro and in vivo evaluation of a novel fluorinated ABP688 derivative for the PET imaging of metabotropic glutamate receptor subtype 5
Abstract
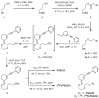
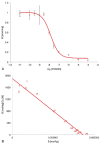
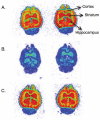
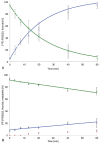
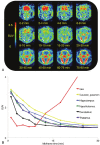
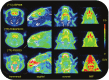
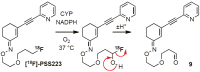
(E)-3-(Pyridin-2-ylethynyl)cyclohex-2-enone O-(2-(3-(18)F-fluoropropoxy)ethyl) oxime ([(18)F]-PSS223) was evaluated in vitro and in vivo to establish its potential as a PET tracer for imaging metabotropic glutamate receptor subtype 5 (mGluR5). [(18)F]-PSS223 was obtained in 20% decay corrected radiochemical yield whereas the non-radioactive PSS223 was accomplished in 70% chemical yield in a S(N)2 reaction of common intermediate mesylate 8 with potassium fluoride. The in vitro binding affinity of [(18)F]-PSS223 was measured directly in a Scatchard assay to give K(d) = 3.34 ± 2.05 nM. [(18)F]-PSS223 was stable in PBS and rat plasma but was significantly metabolized by rat liver microsomal enzymes, but to a lesser extent by human liver microsomes. Within 60 min, 90% and 20% of [(18)F]-PSS223 was metabolized by rat and human microsome enzymes, respectively. In vitro autoradiography on horizontal rat brain slices showed heterogeneous distribution of [(18)F]-PSS223 with the highest accumulation in brain regions where mGluR5 is highly expressed (hippocampus, striatum and cortex). Autoradiography in vitro under blockade conditions with ABP688 confirmed the high specificity of [(18)F]-PSS223 for mGluR5. Under the same blocking conditions but using the mGluR1 antagonist, JNJ16259685, no blockade was observed demonstrating the selectivity of [(18)F]-PSS223 for mGluR5 over mGluR1. Despite favourable in vitro properties of [(18)F]-PSS223, a clear-cut visualization of mGluR5-rich brain regions in vivo in rats was not possible mainly due to a fast clearance from the brain and low metabolic stability of [(18)F]-PSS223.
Keywords: PET imaging; [11C]-ABP688; [18F]-FDEGPECO; [18F]-PSS223; autoradiography; mGluR5; microsome enzymes.
Figures
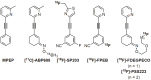
Similar articles
-
In vitro and in vivo evaluation of [18F]-FDEGPECO as a PET tracer for imaging the metabotropic glutamate receptor subtype 5 (mGluR5).Neuroimage. 2011 Jun 1;56(3):984-91. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2011.03.024. Epub 2011 Mar 21. Neuroimage. 2011. PMID: 21406237
-
Radiosynthesis and preclinical evaluation of 11C-ABP688 as a probe for imaging the metabotropic glutamate receptor subtype 5.J Nucl Med. 2006 Apr;47(4):698-705. J Nucl Med. 2006. PMID: 16595505
-
Radiolabeling and in vitro and in vivo evaluation of [18F]-FE-DABP688 as a PET radioligand for the metabotropic glutamate receptor subtype 5.Nucl Med Biol. 2007 Nov;34(8):973-80. doi: 10.1016/j.nucmedbio.2007.07.017. Epub 2007 Sep 19. Nucl Med Biol. 2007. PMID: 17998101
-
(E)-3-(Pyridin-2-ylethynyl)-cyclohex-2-enone-O-2-(2-[18F]fluoroethoxy)ethyl oxime.2011 Jun 5 [updated 2011 Sep 29]. In: Molecular Imaging and Contrast Agent Database (MICAD) [Internet]. Bethesda (MD): National Center for Biotechnology Information (US); 2004–2013. 2011 Jun 5 [updated 2011 Sep 29]. In: Molecular Imaging and Contrast Agent Database (MICAD) [Internet]. Bethesda (MD): National Center for Biotechnology Information (US); 2004–2013. PMID: 21977531 Free Books & Documents. Review.
-
3-(Pyridin-2-ylethynyl)-cyclohex-2-enone-O-[18F]fluoroethyl-oxime.2007 Dec 3 [updated 2008 Jan 28]. In: Molecular Imaging and Contrast Agent Database (MICAD) [Internet]. Bethesda (MD): National Center for Biotechnology Information (US); 2004–2013. 2007 Dec 3 [updated 2008 Jan 28]. In: Molecular Imaging and Contrast Agent Database (MICAD) [Internet]. Bethesda (MD): National Center for Biotechnology Information (US); 2004–2013. PMID: 20641843 Free Books & Documents. Review.
Cited by
-
Preclinical evaluation and test-retest studies of [(18)F]PSS232, a novel radioligand for targeting metabotropic glutamate receptor 5 (mGlu5).Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2015 Jan;42(1):128-37. doi: 10.1007/s00259-014-2883-7. Epub 2014 Aug 20. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2015. PMID: 25139517
-
Multimodality imaging of CXCR4 in cancer: current status towards clinical translation.Curr Mol Med. 2013 Dec;13(10):1538-48. doi: 10.2174/1566524013666131111121325. Curr Mol Med. 2013. PMID: 24206137 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Carbon-fluorine bond cleavage mediated by metalloenzymes.Chem Soc Rev. 2020 Jul 21;49(14):4906-4925. doi: 10.1039/c9cs00740g. Epub 2020 Jun 8. Chem Soc Rev. 2020. PMID: 32510080 Free PMC article. Review.
-
PET imaging of metabotropic glutamate receptor subtype 5 (mGluR5).Am J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2012;2(1):29-32. Epub 2011 Dec 15. Am J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2012. PMID: 23133800 Free PMC article.
-
A Review of Molecular Imaging of Glutamate Receptors.Molecules. 2020 Oct 16;25(20):4749. doi: 10.3390/molecules25204749. Molecules. 2020. PMID: 33081223 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Ametamey SM, Honer M, Schubiger PA. Molecular imaging with PET. Chem Rev. 2008;108:1501–1516. - PubMed
-
- Fowler JS, Volkow ND, Wang GJ, Ding YS, Dewey SL. PET and drug research and development. J Nucl Med. 1999;40:1154–1163. - PubMed
-
- Fowden L. Fluoroamino acids and protein synthesis. Ciba Foundation Symposium, Carbon-Fluorine Compounds. 1972;2:141–159. - PubMed
-
- Weygand F, Oettmeier W. Fluorine-containing amino acids. Russian Chem Rev. 1970;39:290–300.
-
- Masu M, Tanabe Y, Tsuchida K, Shigemoto R, Nakanishi S. Sequence and expression of a metabotropic glutamate receptor. Nature. 1991;349:760–765. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
