Non-invasive longitudinal imaging of tumor progression using an (111)indium labeled CXCR4 peptide antagonist
- PMID: 23133805
- PMCID: PMC3478110
Non-invasive longitudinal imaging of tumor progression using an (111)indium labeled CXCR4 peptide antagonist
Abstract
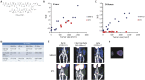
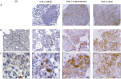
The chemokine receptor 4 (CXCR4) is a biomarker that is over-expressed in ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS). Hence, CXCR4-targeted (molecular) imaging approaches may have diagnostic value in such a challenging, premalignant lesion. The indium labeled CXCR4 peptide-antagonist, (111)In-DTPA-Ac-TZ14011, was used to visualize CXCR4-expression in a mammary intraepithelial neoplastic outgrowth (MIN-O) mouse tumor model resembling human DCIS. MIN-O lesion development was longitudinally monitored using SPET/CT and tracer uptake was compared to uptake in control lesions. Expression of CXCR4 was validated using immunohistochemistry and flow cytometric analysis. The uptake of (111)In-DTPA-Ac-TZ14011 was related to tumor angiogenesis using (111)In-cDTPA-[RGDfK]. Twenty-four hours after tracer injection, MIN-O lesions could be discriminated from low CXCR4-expressing control tumors, while the degree of angiogenesis based on the α(v)β(3) integrin expression in both tumor types was similar. The uptake of (111)In-DTPA-Ac-TZ14011 in early MIN-O lesions was significantly lower than in larger intermediate and late-stage lesions, two-and-a-half-times (p=0.03) and seven-times (p=0.002), respectively. Intermediate and late stage lesions show a higher degree of membranous CXCR4-staining at immunohistochemistry and flow cytometric analysis. From this study we can conclude that (111)In-DTPA-Ac-TZ14011 can be used to visualize the CXCR4-expression in MIN-O lesions longitudinally.
Keywords: Chemokine receptor 4 (CXCR4); ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS); longitudinal imaging; mouse model; single photon emission computed tomography (SPECT); tumor progression.
Figures

References
-
- Donzella GA, Schols D, Lin SW, Esté JA, Nagashima KA, Maddon PJ, Allaway GP, Sakmar TP, Henson G, de Clercq E, Moore JP. AMD3100, a small molecule inhibitor of HIV-1 entry via the CXCR4 co-receptor. Nature Med. 1998;4:71–7. - PubMed
-
- Balkwill F. The significance of cancer cell expression of the chemokine receptor CXCR4. Seminars in Cancer Biology. 2004;14:171–9. - PubMed
-
- Balkwill F. Cancer and the chemokine network. Nature Rev Cancer. 2004;4:540–550. - PubMed
-
- Luker KE, Luker GD. Functions of CXCL12 and CXCR4 in breast cancer. Cancer Letters. 2006;238:30–41. - PubMed
-
- Epstein RJ. The CXCL12-CXCR4 chemotactic pathway as a target of adjuvant breast cancer therapies. Nature Rev Cancer. 2004;4:1–9. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
