Blood-brain barrier dysfunction-induced inflammatory signaling in brain pathology and epileptogenesis
- PMID: 23134494
- PMCID: PMC3703535
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1528-1167.2012.03701.x
Blood-brain barrier dysfunction-induced inflammatory signaling in brain pathology and epileptogenesis
Abstract
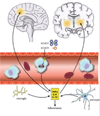
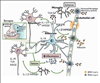
The protection of the brain from blood-borne toxins, proteins, and cells is critical to the brain's normal function. Accordingly, a compromise in the blood-brain barrier (BBB) function accompanies many neurologic disorders, and is tightly associated with brain inflammatory processes initiated by both infiltrating leukocytes from the blood, and activation of glial cells. Those inflammatory processes contribute to determining the severity and prognosis of numerous neurologic disorders, and can both cause, and result from BBB dysfunction. In this review we examine the role of BBB and inflammatory responses, in particular activation of transforming grown factor β (TGFβ) signaling, in epilepsy, stroke, and Parkinson's disease.
Wiley Periodicals, Inc. © 2012 International League Against Epilepsy.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest to disclose. We confirm that we have read the Journal’s position on issues involved in ethical publication and affirm that this report is consistent with those guidelines.
Figures
References
-
- Abbott NJ, Ronnback L, Hansson E. Astrocyte-endothelial inter-actions at the blood–brain barrier. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2006;7:41–53. - PubMed
-
- Aihara N, Hall JJ, Pitts LH, Fukuda K, Noble LJ. Altered immunoexpression of microglia and macrophages after mild head-injury. J Neurotrauma. 1995;12:53–63. - PubMed
-
- Benmoyal-Segal L, Vander T, Shifman S, Bryk B, Ebstein RP, Marcus EL, Stessman J, Darvasi A, Herishanu Y, Friedman A, Soreq H. Acetylcholinesterase/paraoxonase interactions increase the risk of insecticide-induced Parkinson’s disease. Faseb J. 2005;19:452–454. - PubMed

