Cardiac-specific catalase overexpression rescues anthrax lethal toxin-induced cardiac contractile dysfunction: role of oxidative stress and autophagy
- PMID: 23134810
- PMCID: PMC3520786
- DOI: 10.1186/1741-7015-10-134
Cardiac-specific catalase overexpression rescues anthrax lethal toxin-induced cardiac contractile dysfunction: role of oxidative stress and autophagy
Abstract
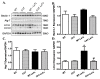
Background: Lethal and edema toxins secreted by Bacillus anthracis during anthrax infection were found to incite serious cardiovascular complications. However, the underlying mechanisms in anthrax lethal toxin-induced cardiac anomalies remain unknown. This study was designed to evaluate the impact of antioxidant enzyme catalase in anthrax lethal toxin-induced cardiomyocyte contractile dysfunction.
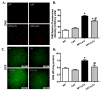
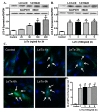
Methods: Wild type (WT) and cardiac-specific catalase overexpression mice were challenged with lethal toxin (2 μg/g, intraperotineally (i.p.)). Cardiomyocyte contractile and intracellular Ca(2+) properties were assessed 18 h later using an IonOptix edge-detection system. Proteasome function was assessed using chymotrypsin-like and caspase-like activities. GFP-LC3 puncta and Western blot analysis were used to evaluate autophagy and protein ubiquitination.
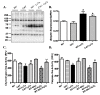
Results: Lethal toxin exposure suppressed cardiomyocyte contractile function (suppressed peak shortening, maximal velocity of shortening/re-lengthening, prolonged duration of shortening/re-lengthening, and impaired intracellular Ca(2+) handling), the effects of which were alleviated by catalase. In addition, lethal toxin triggered autophagy, mitochondrial and ubiquitin-proteasome defects, the effects of which were mitigated by catalase. Pretreatment of cardiomyocytes from catalase mice with the autophagy inducer rapamycin significantly attenuated or ablated catalase-offered protection against lethal toxin-induced cardiomyocyte dysfunction. On the other hand, the autophagy inhibitor 3-MA ablated or significantly attenuated lethal toxin-induced cardiomyocyte contractile anomalies.
Conclusions: Our results suggest that catalase is protective against anthrax lethal toxin-induced cardiomyocyte contractile and intracellular Ca(2+) anomalies, possibly through regulation of autophagy and mitochondrial function.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Toll-like receptor 4 knockout protects against anthrax lethal toxin-induced cardiac contractile dysfunction: role of autophagy.Br J Pharmacol. 2012 Oct;167(3):612-26. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.2012.02040.x. Br J Pharmacol. 2012. PMID: 22612289 Free PMC article.
-
Anthrax lethal toxin suppresses murine cardiomyocyte contractile function and intracellular Ca2+ handling via a NADPH oxidase-dependent mechanism.PLoS One. 2010 Oct 13;5(10):e13335. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0013335. PLoS One. 2010. PMID: 20967205 Free PMC article.
-
Antioxidant catalase rescues against high fat diet-induced cardiac dysfunction via an IKKβ-AMPK-dependent regulation of autophagy.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2015 Feb;1852(2):343-52. doi: 10.1016/j.bbadis.2014.06.027. Epub 2014 Jun 30. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2015. PMID: 24993069
-
New insights into the functions of anthrax toxin.Expert Rev Mol Med. 2006 Apr 11;8(7):1-18. doi: 10.1017/S1462399406010714. Expert Rev Mol Med. 2006. PMID: 16608555 Review.
-
The Potential Pathogenic Contributions of Endothelial Barrier and Arterial Contractile Dysfunction to Shock Due to B. anthracis Lethal and Edema Toxins.Toxins (Basel). 2017 Dec 6;9(12):394. doi: 10.3390/toxins9120394. Toxins (Basel). 2017. PMID: 29210983 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Therapeutic potentials of catalase: Mechanisms, applications, and future perspectives.Int J Health Sci (Qassim). 2024 Mar-Apr;18(2):1-6. Int J Health Sci (Qassim). 2024. PMID: 38455600 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Estrogen receptor ERα plays a major role in ethanol-evoked myocardial oxidative stress and dysfunction in conscious female rats.Alcohol. 2016 Feb;50:27-35. doi: 10.1016/j.alcohol.2015.11.002. Epub 2015 Nov 26. Alcohol. 2016. PMID: 26695589 Free PMC article.
-
Influence of sex on cardiovascular drug responses: role of estrogen.Curr Opin Pharmacol. 2017 Apr;33:1-5. doi: 10.1016/j.coph.2017.02.002. Epub 2017 Mar 21. Curr Opin Pharmacol. 2017. PMID: 28340373 Free PMC article. Review.
-
B. anthracis associated cardiovascular dysfunction and shock: the potential contribution of both non-toxin and toxin components.BMC Med. 2013 Oct 9;11:217. doi: 10.1186/1741-7015-11-217. BMC Med. 2013. PMID: 24107194 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Does Bacillus anthracis Lethal Toxin Directly Depress Myocardial Function? A Review of Clinical Cases and Preclinical Studies.Toxins (Basel). 2015 Dec 12;7(12):5417-34. doi: 10.3390/toxins7124891. Toxins (Basel). 2015. PMID: 26703730 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Borio L, Frank D, Mani V, Chiriboga C, Pollanen M, Ripple M, Ali S, DiAngelo C, Lee J, Arden J, Titus J, Fowler D, O'Toole T, Masur H, Bartlett J, Inglesby T. Death due to bioterrorism-related inhalational anthrax: report of 2 patients. JAMA. 2001;286:2554–2559. doi: 10.1001/jama.286.20.2554. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Holty JE, Bravata DM, Liu H, Olshen RA, McDonald KM, Owens DK. Systematic review: a century of inhalational anthrax cases from 1900 to 2005. Ann Intern Med. 2006;144:270–280. - PubMed
-
- Cui X, Moayeri M, Li Y, Li X, Haley M, Fitz Y, Correa-Araujo R, Banks SM, Leppla SH, Eichacker PQ. Lethality during continuous anthrax lethal toxin infusion is associated with circulatory shock but not inflammatory cytokine or nitric oxide release in rats. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2004;286:R699–709. doi: 10.1152/ajpregu.00593.2003. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

