RhoB differentially controls Akt function in tumor cells and stromal endothelial cells during breast tumorigenesis
- PMID: 23135917
- PMCID: PMC4201498
- DOI: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-11-3055
RhoB differentially controls Akt function in tumor cells and stromal endothelial cells during breast tumorigenesis
Abstract
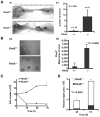
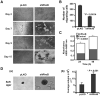
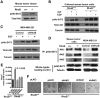
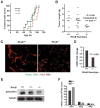
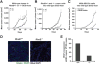
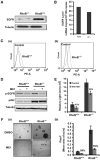
Tumors are composed of cancer cells but also a larger number of diverse stromal cells in the tumor microenvironment. Stromal cells provide essential supports to tumor pathophysiology but the distinct characteristics of their signaling networks are not usually considered in developing drugs to target tumors. This oversight potentially confounds proof-of-concept studies and increases drug development risks. Here, we show in established murine and human models of breast cancer how differential regulation of Akt by the small GTPase RhoB in cancer cells or stromal endothelial cells determines their dormancy versus outgrowth when angiogenesis becomes critical. In cancer cells in vitro or in vivo, RhoB functions as a tumor suppressor that restricts EGF receptor (EGFR) cell surface occupancy as well as Akt signaling. However, after activation of the angiogenic switch, RhoB functions as a tumor promoter by sustaining endothelial Akt signaling, growth, and survival of stromal endothelial cells that mediate tumor neoangiogenesis. Altogether, the positive impact of RhoB on angiogenesis and progression supercedes its negative impact in cancer cells themselves. Our findings elucidate the dominant positive role of RhoB in cancer. More generally, they illustrate how differential gene function effects on signaling pathways in the tumor stromal component can complicate the challenge of developing therapeutics to target cancer pathophysiology.
Conflict of interest statement
The Editor-in-Chief of
Figures

Similar articles
-
The RAS-related GTPase RHOB confers resistance to EGFR-tyrosine kinase inhibitors in non-small-cell lung cancer via an AKT-dependent mechanism.EMBO Mol Med. 2017 Feb;9(2):238-250. doi: 10.15252/emmm.201606646. EMBO Mol Med. 2017. PMID: 28003335 Free PMC article.
-
Akt mediates Ras downregulation of RhoB, a suppressor of transformation, invasion, and metastasis.Mol Cell Biol. 2004 Jun;24(12):5565-76. doi: 10.1128/MCB.24.12.5565-5576.2004. Mol Cell Biol. 2004. PMID: 15169915 Free PMC article.
-
Geranylgeranylated, but not farnesylated, RhoB suppresses Ras transformation of NIH-3T3 cells.Exp Cell Res. 2005 Apr 1;304(2):354-64. doi: 10.1016/j.yexcr.2004.10.019. Epub 2004 Dec 28. Exp Cell Res. 2005. PMID: 15748883
-
Tumor-associated stromal cells as key contributors to the tumor microenvironment.Breast Cancer Res. 2016 Aug 11;18(1):84. doi: 10.1186/s13058-016-0740-2. Breast Cancer Res. 2016. PMID: 27515302 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Pten in the breast tumor microenvironment: modeling tumor-stroma coevolution.Cancer Res. 2011 Feb 15;71(4):1203-7. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-10-3263. Epub 2011 Feb 8. Cancer Res. 2011. PMID: 21303970 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Mutant HRas Signaling and Rationale for Use of Farnesyltransferase Inhibitors in Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma.Target Oncol. 2023 Sep;18(5):643-655. doi: 10.1007/s11523-023-00993-3. Epub 2023 Sep 4. Target Oncol. 2023. PMID: 37665491 Review.
-
Minireview: Mouse Models of Rho GTPase Function in Mammary Gland Development, Tumorigenesis, and Metastasis.Mol Endocrinol. 2016 Mar;30(3):278-89. doi: 10.1210/me.2015-1294. Epub 2015 Dec 17. Mol Endocrinol. 2016. PMID: 26677753 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Rho GTPases: Big Players in Breast Cancer Initiation, Metastasis and Therapeutic Responses.Cells. 2020 Sep 25;9(10):2167. doi: 10.3390/cells9102167. Cells. 2020. PMID: 32992837 Free PMC article. Review.
-
MiR-21-5p knockdown inhibits epithelial to mesenchymal transition in A549 lung adenocarcinoma cells by upregulating RhoB.Mol Biol Rep. 2024 Jul 23;51(1):837. doi: 10.1007/s11033-024-09794-x. Mol Biol Rep. 2024. PMID: 39042337
-
The c-Jun/RHOB/AKT pathway confers resistance of BRAF-mutant melanoma cells to MAPK inhibitors.Oncotarget. 2015 Jun 20;6(17):15250-64. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.3888. Oncotarget. 2015. PMID: 26098773 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Pietras K, Ostman A. Hallmarks of cancer: interactions with the tumor stroma. Exp Cell Res. 2010;316:1324–31. - PubMed
-
- McAllister SS, Weinberg RA. Tumor-host interactions: a far-reaching relationship. J Clin Oncol. 2010;28:4022–8. - PubMed
-
- Hanahan D, Folkman J. Patterns and emerging mechanisms of the angiogenic switch during tumorigenesis. Cell. 1996;86:353–64. - PubMed
-
- Mueller MM, Fusenig NE. Friends or foes - bipolar effects of the tumour stroma in cancer. Nat Rev Cancer. 2004;4:839–49. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

