Interactions between chemical and climate stressors: a role for mechanistic toxicology in assessing climate change risks
- PMID: 23136056
- PMCID: PMC3601417
- DOI: 10.1002/etc.2043
Interactions between chemical and climate stressors: a role for mechanistic toxicology in assessing climate change risks
Abstract
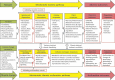
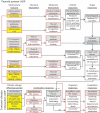
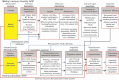
Incorporation of global climate change (GCC) effects into assessments of chemical risk and injury requires integrated examinations of chemical and nonchemical stressors. Environmental variables altered by GCC (temperature, precipitation, salinity, pH) can influence the toxicokinetics of chemical absorption, distribution, metabolism, and excretion as well as toxicodynamic interactions between chemicals and target molecules. In addition, GCC challenges processes critical for coping with the external environment (water balance, thermoregulation, nutrition, and the immune, endocrine, and neurological systems), leaving organisms sensitive to even slight perturbations by chemicals when pushed to the limits of their physiological tolerance range. In simplest terms, GCC can make organisms more sensitive to chemical stressors, while alternatively, exposure to chemicals can make organisms more sensitive to GCC stressors. One challenge is to identify potential interactions between nonchemical and chemical stressors affecting key physiological processes in an organism. We employed adverse outcome pathways, constructs depicting linkages between mechanism-based molecular initiating events and impacts on individuals or populations, to assess how chemical- and climate-specific variables interact to lead to adverse outcomes. Case examples are presented for prospective scenarios, hypothesizing potential chemical-GCC interactions, and retrospective scenarios, proposing mechanisms for demonstrated chemical-climate interactions in natural populations. Understanding GCC interactions along adverse outcome pathways facilitates extrapolation between species or other levels of organization, development of hypotheses and focal areas for further research, and improved inputs for risk and resource injury assessments.
Copyright © 2012 SETAC.
Figures

References
-
- Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change. 2007. Climate Change 2007: Synthesis Report. Contribution of Working Groups I, II, and III to the Fourth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change. Geneva, Switzerland.
-
- Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change. Climate Change 2007: Impacts, Adaptation, and Vulnerability. Contribution of Working Group II to the Fourth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change. Cambridge, UK: Cambridge University Press; 2007.
-
- Harley CDG, Hughes AR, Hultgren KM, Miner BG, Sorte CJB, Thornber CS, Rodriguez LF, Tomanek L, Williams SL. The impacts of climate change in coastal marine systems. Ecol Lett. 2006;9:228–241. - PubMed
-
- Heino J, Virkkala R, Toivonen H. Climate change and freshwater biodiversity: Detected patterns, future trends and adaptations in northern regions. Biol Rev. 2009;84:39–54. - PubMed
-
- Rijnsdorp AD, Peck MA, Engelhard GH, Moellmann C, Pinnegar JK. Resolving the effect of climate change on fish populations. ICES J Mar Sci. 2009;66:1570–1583.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

