Long-term changes in trigeminal ganglionic and thalamic neuronal activities following inferior alveolar nerve transection in behaving rats
- PMID: 23136441
- PMCID: PMC6621638
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1828-12.2012
Long-term changes in trigeminal ganglionic and thalamic neuronal activities following inferior alveolar nerve transection in behaving rats
Abstract
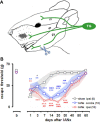
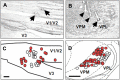
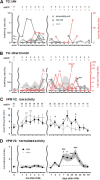
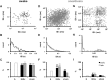
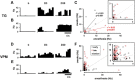
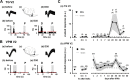
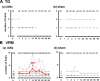
The transection of the inferior alveolar nerve (IANx) produces allodynia in the whisker pad (V2 division) of rats. Ectopic discharges from injured trigeminal ganglion (TG) neurons and thalamocortical reorganization are possible contributors to the sensitization of uninjured V2 primary and CNS neurons. To test which factor is more important, TG and ventroposterior medial nucleus (VPM) neurons were longitudinally followed before, during, and after IANx for up to 80 d. Spontaneous discharges and mechanical stimulation-evoked responses were recorded in conscious and in anesthetized states. Results show (1) a sequential increase in spontaneous activities, first in the injured TG neurons of the IAN (2-30 d), followed by uninjured V2 ganglion neurons (6-30 d), and then VPM V2 neurons (7-30 d) after IANx; (2) ectopic discharges included burst and regular firing patterns in the IAN and V2 branches of the TG neurons; and (3) the receptive field expanded, the modality shifted, and long-lasting after-discharges occurred only in VPM V2 neurons. All of these changes appeared in the late or maintenance phase (7-30 d) and disappeared during the recovery phase (40-60 d). These observations suggest that ectopic barrages in the injured IAN contribute more to the development of sensitization, whereas the modality shift and evoked after-discharges in the VPM thalamic neurons contribute more to the maintenance phase of allodynia by redirecting tactile information to the cortex as nociceptive.
Figures




References
-
- Adrian ED. The effects of injury on mammalian nerve fibres. Proc Roy Soc Ser B. 1930;106:596–618.
-
- Barbay S, Peden EK, Falchook G, Nudo RJ. Sensitivity of neurons in somatosensory cortex (S1) to cutaneous stimulation of the hindlimb immediately following a sciatic nerve crush. Somatosens Mot Res. 1999;16:103–114. - PubMed
-
- Baron R. Mechanisms of disease: neuropathic pain—a clinical perspective. Nat Clin Pract Neurol. 2006;2:95–106. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
