Neural synchronization during face-to-face communication
- PMID: 23136442
- PMCID: PMC6621612
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2926-12.2012
Neural synchronization during face-to-face communication
Abstract
Although the human brain may have evolutionarily adapted to face-to-face communication, other modes of communication, e.g., telephone and e-mail, increasingly dominate our modern daily life. This study examined the neural difference between face-to-face communication and other types of communication by simultaneously measuring two brains using a hyperscanning approach. The results showed a significant increase in the neural synchronization in the left inferior frontal cortex during a face-to-face dialog between partners but none during a back-to-back dialog, a face-to-face monologue, or a back-to-back monologue. Moreover, the neural synchronization between partners during the face-to-face dialog resulted primarily from the direct interactions between the partners, including multimodal sensory information integration and turn-taking behavior. The communicating behavior during the face-to-face dialog could be predicted accurately based on the neural synchronization level. These results suggest that face-to-face communication, particularly dialog, has special neural features that other types of communication do not have and that the neural synchronization between partners may underlie successful face-to-face communication.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no financial conflicts of interest.
Figures
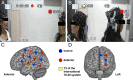
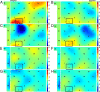


Comment in
-
On the same wavelength: face-to-face communication increases interpersonal neural synchronization.J Neurosci. 2013 Mar 20;33(12):5081-2. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0063-13.2013. J Neurosci. 2013. PMID: 23516273 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Belin P, Fecteau S, Bédard C. Thinking the voice: neural correlates of voice perception. Trends Cogn Sci. 2004;8:129–135. - PubMed
-
- Boaz NT, Almquist AJ. Biological anthropology: a synthetic approach to human evolution. Upper Saddle River, NJ: Prentice Hall; 1997.
-
- Bordia P. Face-to-face versus computer-mediated communication: a synthesis of the experimental literature. J Bus Commun. 1997;34:99.
-
- Corina DP, Knapp H. Special issue: review sign language processing and the mirror neuron system. Cortex. 2006;42:529–539. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
