Potential of a mutant-based reverse genetic approach for functional genomics and molecular breeding in soybean
- PMID: 23136486
- PMCID: PMC3406801
- DOI: 10.1270/jsbbs.61.462
Potential of a mutant-based reverse genetic approach for functional genomics and molecular breeding in soybean
Abstract
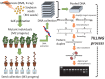
Mutant-based reverse genetics offers a powerful way to create novel mutant alleles at a selected locus. This approach makes it possible to directly identify plants that carry a specific modified gene from the nucleotide sequence data. Soybean [Glycine max (L.) Merr.] has a highly redundant paleopolyploid genome (approx. 1.1 Gb), which was completely sequenced in 2010. Using reverse genetics to support functional genomics studies designed to predict gene function would accelerate post-genomics research in soybean. Furthermore, the novel mutant alleles created by this approach would be useful genetic resources for improving various traits in soybean. A reverse genetic screening platform in soybean has been developed that combines more than 40,000 mutant lines with a high-throughput method, Targeting Local Lesions IN Genome (TILLING). In this review, the mutant-based reverse genetic approach based on this platform is described, and the likely evolution of this approach in the near future.
Keywords: TILLING; mutagenesis; reverse genetics; soybean.
Figures

References
-
- Anai T, Yamada T, Kinoshita T, Rahman SM, Takagi Y. Identification of corresponding genes for three low-α-linolenic acid mutants and elucidation of their contribution to fatty acid biosynthesis in soybean seed. Plant Sci. 2005;168:1615–1623.
-
- Anai T, Yamada T, Hideshima R, Kinoshita T, Rahman SM, Takagi Y. Two high-oleic-acid soybean mutants, M23 and KK21, have disrupted microsomal omega-6 fatty acid desaturase, encoded by GmFAD2-1a. Breed Sci. 2008;58:447–452.
-
- Ansorge WJ. Next-generation DNA sequencing techniques. New Biotech. 2009;25:195–203. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
