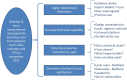
What is the NHS Safety Thermometer?
- PMID: 23136533
- PMCID: PMC3484316
- DOI: 10.1258/cr.2012.012038
What is the NHS Safety Thermometer?
Abstract
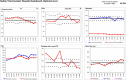
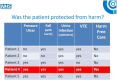
The English National Health Service (NHS) announced a new programme to incentivize use of the NHS Safety Thermometer (NHS ST) in the NHS Operating Framework for 2012/13. For the first time, the NHS is using the Commissioning for Quality and Innovation (CQUIN) scheme, a contract lever, to incentivize ALL providers of NHS care to measure four common complications (harms) using the NHS ST in a proactive way on one day per month. This national CQUIN scheme provides financial reward for the collection of baseline data with a view to incentivizing the achievement of improvement goals in later years. In this paper, we describe the rationale for this large-scale data collection, the purpose of the instrument and its potential contribution to our current understanding of patient safety. It is not a comprehensive description of the method or preliminary data. This will be published separately. The focus of the NHS ST on pressure ulcers, falls, catheters and urine infection and venous thromboembolism is broadly applicable to patients across all healthcare settings, but is specifically pertinent to older people who, experiencing more healthcare intervention, are at risk of not one but multiple harms. In this paper, we also describe an innovative patient-level composite measure of the absence of harm from the four identified, termed as "harmfreecare" which is unique to the NHS ST and is under development to raise standards for patient safety.
Figures
References
-
- DH. The Operating Framework for the NHS in England 2012–13. London: DH, 2011. See http://www.dh.gov.uk/en/Publicationsandstatistics/Publications/Publicati... Last accessed on 15th August 2012
-
- DH. Delivering the NHS safety thermometer CQUIN 2012/13: A Preliminary Guide to Measuring ‘Harm Free’ Care. London: DH, 2012. See http://www.dh.gov.uk/en/Publicationsandstatistics/Publications/Publicati... Last accessed on 15th August 2012
-
- DH. Using the Commissioning for Quality and Innovation (CQUIN) payment framework. London: DH; 2008. See http://www.dh.gov.uk/en/Publicationsandstatistics/Publications/Publicati... Last accessed on 15th August 2012
-
- Personal correspondence to authors (Stewart K, Brotherton A, Power M) via the Safety Express and NHS partner communities 2011–12
-
- DH. An Organisation with a Memory. London: DH, 2000. See http://www.dh.gov.uk/en/Publicationsandstatistics/Publications/Publicati... Last accessed on 15th August 2012
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
