IL-6 trans-signaling via the soluble IL-6 receptor: importance for the pro-inflammatory activities of IL-6
- PMID: 23136552
- PMCID: PMC3491447
- DOI: 10.7150/ijbs.4989
IL-6 trans-signaling via the soluble IL-6 receptor: importance for the pro-inflammatory activities of IL-6
Abstract
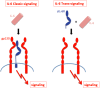
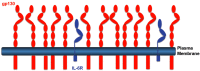
Interleukin-6 (IL-6) is a cytokine with many activities. It has functions in the regulation of the immune system and the nervous system. Furthermore, IL-6 is involved in liver regeneration and in the metabolic control of the body. On target cells, IL-6 binds to an 80 kDa IL-6 receptor (IL-6R). The complex of IL-6 and IL-6R associates with a second protein, gp130, which thereupon dimerizes and initiates intracellular signaling. Whereas gp130 is expressed on all cells, IL-6R is only present on few cells in the body including hepatocytes and some leukocytes. Cells, which do not express IL-6R cannot respond to the cytokine, since gp130 alone has no measurable affinity for IL-6. Interestingly, a soluble form of IL-6R (sIL-6R) comprising the extracellular portion of the receptor can bind IL-6 with a similar affinity as the membrane bound IL-6R. The complex of IL-6 and sIL-6R can bind to gp130 on cells, which do not express the IL-6R, and which are unresponsive to IL-6. This process has been called trans-signaling. Here I will review published evidence that IL-6 trans-signaling is pro-inflammatory whereas classic IL-6 signaling via the membrane bound IL-6R is needed for regenerative or anti-inflammatory activities of the cytokine. Furthermore, the detailed knowledge of IL-6 biology has important consequences for therapeutic strategies aimed at the blockade of the cytokine IL-6.
Keywords: IL-6; IL-6 receptor; inflammation; inflammation associated cancer.; shedding; soluble receptor.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interests: Dr. Rose-John is an inventor on patents describing the function of sgp130Fc. He is also a shareholder of the CONARIS Research Institute (Kiel, Germany), which is commercially developing sgp130Fc proteins as therapeutics for inflammatory diseases.
Figures


References
-
- Hirano T, Yasukawa K, Harada H, Taga T, Watanabe Y, Matsuda T. et al. Complementary DNA for a novel human interleukin (BSF-2) that induces B lymphocytes to produce immunoglobulin. Nature. 1986;324:73–6. - PubMed
-
- Bazan JF. Haemopoietic receptors and helical cytokines. Immunol Today. 1990;11:350–4. - PubMed
-
- Yamasaki K, Taga T, Hirata Y, Yawata H, Kawanishi Y, Seed B. et al. Cloning and expression of the human interleukin-6 (BSF-2/IFN beta 2) receptor. Science. 1988;241:825–8. - PubMed
-
- Hibi M, Murakami M, Saito M, Hirano T, Taga T, Kishimoto T. Molecular cloning and expression of an IL-6 signal transducer, gp130. Cell. 1990;63:1149–57. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

