D-amino acids boost the selectivity and confer supramolecular hydrogels of a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID)
- PMID: 23136972
- PMCID: PMC3547157
- DOI: 10.1021/ja310019x
D-amino acids boost the selectivity and confer supramolecular hydrogels of a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID)
Abstract
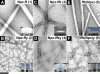
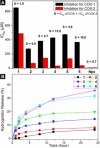
As systemically used therapeutics for treating acute or chronic pains or inflammations, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) also associate with the adverse gastrointestinal and renal effects and cardiovascular risks. Thus, it is beneficial to develop topical gels that selectively inhibit cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2) for the management of local inflammation. In this work, we demonstrate that the covalent conjugation of d-amino acids to naproxen (i.e., a NSAID) not only affords supramolecular hydrogelators for the topical gels but also unexpectedly and significantly elevates the selectivity toward COX-2 about 20× at little expense of the activity of naproxen. This work illustrates a previously unexplored approach that employs d-amino acids for the development of functional molecules that have dual or multiple roles and exceptional biostability, which offers a new class of molecular hydrogels of therapeutic agents.
Figures


References
-
- Silverstein FE, Faich G, Goldstein JL, Simon LS, Pincus T, Whelton A, Makuch R, Eisen G, Agarwal NM, Stenson WF, Burr AM, Zhao WW, Kent JD, Lefkowith JB, Verburg KM, Geis GS. JAMA-J. Am. Med. Assoc. 2000;284:1247–1255. - PubMed
-
- Catella-Lawson F, Reilly MP, Kapoor SC, Cucchiara AJ, DeMarco S, Tournier B, Vyas SN, FitzGerald GA. N. Engl. J. Med. 2001;345:1809–1817. - PubMed
-
- Bresalier RS, Sandler RS, Quan H, Bolognese JA, Oxenius B, Horgan K, Lines C, Riddell R, Morton D, Lanas A, Konstam MA, Baron JA, Investigators APT. N. Engl. J. Med. 2005;352:1092–1102. - PubMed
-
- Banning M. Expert Opin. Pharmacotherapy. 2008;9:2921–2929. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

