Targeting TIM-1 on CD4 T cells depresses macrophage activation and overcomes ischemia-reperfusion injury in mouse orthotopic liver transplantation
- PMID: 23137033
- PMCID: PMC3535503
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1600-6143.2012.04316.x
Targeting TIM-1 on CD4 T cells depresses macrophage activation and overcomes ischemia-reperfusion injury in mouse orthotopic liver transplantation
Abstract
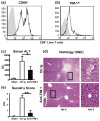
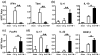
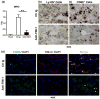
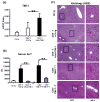
Hepatic injury due to cold storage followed by reperfusion remains a major cause of morbidity and mortality after orthotopic liver transplantation (OLT). CD4 T cell TIM-1 signaling costimulates a variety of immune responses in allograft recipients. This study analyzes mechanisms by which TIM-1 affects liver ischemia-reperfusion injury (IRI) in a murine model of prolonged cold storage followed by OLT. Livers from C57BL/6 mice, preserved at 4°C in the UW solution for 20 h, were transplanted to syngeneic recipients. There was an early (1 h) increased accumulation of TIM-1+ activated CD4 T cells in the ischemic OLTs. Disruption of TIM-1 signaling with a blocking mAb (RMT1-10) ameliorated liver damage, evidenced by reduced sALT levels and well-preserved architecture. Unlike in controls, TIM-1 blockade diminished OLT expression of Tbet/IFN-γ, but amplified IL-4/IL-10/IL-22; abolished neutrophil and macrophage infiltration/activation and inhibited NF-κB while enhancing Bcl-2/Bcl-xl. Although adoptive transfer of CD4 T cells triggered liver damage in otherwise IR-resistant RAG(-/-) mice, adjunctive TIM-1 blockade reduced Tbet transcription and abolished macrophage activation, restoring homeostasis in IR-stressed livers. Further, transfer of TIM-1(Hi) CD4+, but not TIM-1(Lo) CD4+ T cells, recreated liver IRI in RAG(-/-) mice. Thus, TIM-1 expressing CD4 T cells are required in the mechanism of innate immune-mediated hepatic IRI in OLTs.
© Copyright 2012 The American Society of Transplantation and the American Society of Transplant Surgeons.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


References
-
- Caldwell CC, Tschoep J, Lentsch AB. Lymphocyte function during hepatic ischemia/reperfusion injury. J Leukoc Biol. 2007;82:457–464. - PubMed
-
- Shen XD, Ke B, Zhai Y, et al. Stat4 and Stat6 signaling in hepatic ischemia/reperfusion injury in mice: HO-1 dependence of Stat4 disruption-mediated cytoprotection. Hepatology. 2003;37:296–303. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

