Demographic, metabolic, and blood pressure characteristics of living kidney donors spanning five decades
- PMID: 23137211
- PMCID: PMC3558745
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1600-6143.2012.04321.x
Demographic, metabolic, and blood pressure characteristics of living kidney donors spanning five decades
Abstract
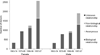
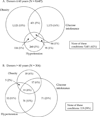
While cautious criteria for selection of living kidney donors are credited for favorable outcomes, recent practice changes may include acceptance of less than ideal donors. To characterize trends in donor acceptance, the Renal and Lung Living Donors Evaluation (RELIVE) Study evaluated 8,951 kidney donors who donated between 1963 and 2007 at three major U.S. transplant centers. Over the study interval, there was an increase in the percentage of donors >40 years old from 38% to 51%; donors >60 years varied between 1% and 4%. The proportion of donors with obesity increased from 8% to 26% and with glucose intolerance from 9% to 25%. The percentage of hypertensive donors was consistent (5-8%). Accepted donors ≥60 years old were more likely to have obesity, glucose intolerance, and/or hypertension compared to younger donors (p<0.0001). Our results demonstrate important trends in acceptance of older and more obese donors. The fraction of older donors accepted with glucose intolerance or hypertension remains small and for the majority includes mild elevations in glucose or blood pressure that were previously classified as within normal limits.
© Copyright 2012 The American Society of Transplantation and the American Society of Transplant Surgeons.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosure
The authors of the manuscript have no conflicts of interest to disclose as described by the
Figures

Similar articles
-
Risk-Factor Profile of Living Kidney Donors: The Australia and New Zealand Dialysis and Transplant Living Kidney Donor Registry 2004-2012.Transplantation. 2016 Jun;100(6):1278-83. doi: 10.1097/TP.0000000000000877. Transplantation. 2016. PMID: 27123877
-
Temporal trends, center-level variation, and the impact of prevalent state obesity rates on acceptance of obese living kidney donors.Am J Transplant. 2018 Mar;18(3):642-649. doi: 10.1111/ajt.14519. Epub 2017 Oct 30. Am J Transplant. 2018. PMID: 28949096
-
Implications of excess weight on kidney donation: Long-term consequences of donor nephrectomy in obese donors.Surgery. 2018 Nov;164(5):1071-1076. doi: 10.1016/j.surg.2018.07.015. Epub 2018 Aug 24. Surgery. 2018. PMID: 30149934
-
Expanding criteria for living kidney donors: what are the limits?Transplant Rev (Orlando). 2008 Jul;22(3):187-91. doi: 10.1016/j.trre.2008.04.005. Epub 2008 May 14. Transplant Rev (Orlando). 2008. PMID: 18631876 Review.
-
Latest developments in living kidney donation.Curr Opin Organ Transplant. 2020 Feb;25(1):74-79. doi: 10.1097/MOT.0000000000000724. Curr Opin Organ Transplant. 2020. PMID: 31833966 Review.
Cited by
-
Assessment of Postdonation Outcomes in US Living Kidney Donors Using Publicly Available Data Sets.JAMA Netw Open. 2019 Apr 5;2(4):e191851. doi: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2019.1851. JAMA Netw Open. 2019. PMID: 30977847 Free PMC article.
-
The Association between Body Composition Measurements and Surgical Complications after Living Kidney Donation.J Clin Med. 2021 Jan 5;10(1):155. doi: 10.3390/jcm10010155. J Clin Med. 2021. PMID: 33466272 Free PMC article.
-
Consistency of racial variation in medical outcomes among publicly and privately insured living kidney donors.Transplantation. 2014 Feb 15;97(3):316-24. doi: 10.1097/01.TP.0000436731.23554.5e. Transplantation. 2014. PMID: 24192712 Free PMC article.
-
Obesity and long-term mortality risk among living kidney donors.Surgery. 2019 Aug;166(2):205-208. doi: 10.1016/j.surg.2019.03.016. Epub 2019 May 7. Surgery. 2019. PMID: 31072668 Free PMC article.
-
Early Complications in Kidney Donors and Course of Health-related Quality of Life 12 mo After Donation: An Analysis of the Swiss Organ Living-Donor Health Registry.Transplant Direct. 2024 Oct 10;10(11):e1716. doi: 10.1097/TXD.0000000000001716. eCollection 2024 Nov. Transplant Direct. 2024. PMID: 39399060 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Fehrman-Ekholm I, Elinder CG, Stenbeck M, Tyden G, Groth CG. Kidney donors live longer. Transplantation. 1997;64(7):976–978. - PubMed
-
- Segev DL, Muzaale AD, Caffo BS, Mehta SH, Singer AL, Taranto SE, et al. Perioperative mortality and long-term survival following live kidney donation. JAMA. 2010;303(10):959–966. - PubMed
-
- Ramcharan T, Matas AJ. Long-Term (20–37 years) follow-up of living kidney donors. Am J Transplant. 2002;2:959–964. - PubMed
-
- Najarian JS, Chavers BM, McHugh LE, Matas AJ. 20 years or more of follow-up of living kidney donors. Lancet. 1992;340(8823):807–810. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

