Transcranial direct current stimulation (tDCS) and language
- PMID: 23138766
- PMCID: PMC3717599
- DOI: 10.1136/jnnp-2012-302825
Transcranial direct current stimulation (tDCS) and language
Abstract
Transcranial direct current stimulation (tDCS), a non-invasive neuromodulation technique inducing prolonged brain excitability changes and promoting cerebral plasticity, is a promising option for neurorehabilitation. Here, we review progress in research on tDCS and language functions and on the potential role of tDCS in the treatment of post-stroke aphasia. Currently available data suggest that tDCS over language-related brain areas can modulate linguistic abilities in healthy individuals and can improve language performance in patients with aphasia. Whether the results obtained in experimental conditions are functionally important for the quality of life of patients and their caregivers remains unclear. Despite the fact that important variables are yet to be determined, tDCS combined with rehabilitation techniques seems a promising therapeutic option for aphasia.
Keywords: Aphasia; Electrical Stimulation; Rehabilitation; Speech Therapy; Stroke.
Figures
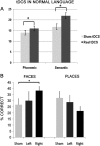
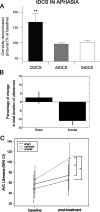

References
-
- Chomsky N. Language and mind. New York: Harcourt, Brace & World, 1968
-
- Saur D, Hartwigsen G. Neurobiology of language recovery after stroke: lessons from neuroimaging studies. Arch Phys Med Rehabil 2012;93:S15–25 - PubMed
-
- Penfield W. Conditioning the uncommitted cortex for language learning. Brain 1965;88:787–98 - PubMed
-
- Ojemann GA. Brain organization for language from the perspective of electrical stimulation mapping. Behav Brain Sci 1983;6:189–230
-
- Ojemann GA. Functional mapping of cortical language areas in adults. Intraoperative approaches. Adv Neurol 1993;63:155–63 - PubMed
