Cytoplasmic ATP hydrolysis powers transport of lipopolysaccharide across the periplasm in E. coli
- PMID: 23138981
- PMCID: PMC3552488
- DOI: 10.1126/science.1228984
Cytoplasmic ATP hydrolysis powers transport of lipopolysaccharide across the periplasm in E. coli
Abstract
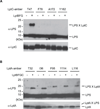
Millions of molecules of lipopolysaccharide (LPS) must be assembled on the Escherichia coli cell surface each time the cell divides. The biogenesis of LPS requires seven essential lipopolysaccharide transport (Lpt) proteins to move LPS from the inner membrane through the periplasm to the cell surface. However, no intermediate transport states have been observed. We developed methods to observe intermediate LPS molecules bound to Lpt proteins in the process of being transported in vivo. Movement of individual LPS molecules along these binding sites required multiple rounds of adenosine triphosphate (ATP) hydrolysis in vitro, which suggests that ATP is used to push a continuous stream of LPS through a transenvelope bridge in discrete steps against a concentration gradient.
Figures



References
-
- Narita S, Tokuda H. Biochemical characterization of an ABC transporter LptBFGC complex required for the outer membrane sorting of lipopolysaccharides. FEBS Lett. 2009;583:2160. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

