Structural insight into the separate roles of inositol tetraphosphate and deacetylase-activating domain in activation of histone deacetylase 3
- PMID: 23139175
- PMCID: PMC3575863
- DOI: 10.1002/pro.2190
Structural insight into the separate roles of inositol tetraphosphate and deacetylase-activating domain in activation of histone deacetylase 3
Abstract
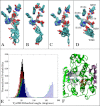
Histone deacetylases (HDACs) repress transcription by deacetylating acetyllysines on specific histone tails. HDAC3 is implicated in neurodegenerative diseases, certain leukemias, and even in disrupting HIV-1 latency. A recent crystal structure of HDAC3 in complex with the deacetylase-activating domain (DAD) of its corepressor complex revealed an inositol tetraphosphate (IP4) molecule at the protein-protein interface. IP4 was shown to play an important, yet mechanistically ambiguous, role in the activity of HDAC3. The goal of this article is to explore the conformational ensemble of HDAC3 in its inactive apo state and in the presence of each or both of DAD and IP4. Using triplicate, 100 ns molecular dynamic simulations, we study the apo, ternary, and intermediate DAD-bound or IP4-bound HDAC3 states. We find that a population-shift effect is induced by the presence of each corepressor, and is most notable in the presence of both. Our results offer new insights into the change in dynamics necessary for the activation of HDAC3 and highlight the roles of IP4 and DAD in this process.
Copyright © 2012 The Protein Society.
Figures


References
-
- Bhaskara S, Knutson SK, Jiang G, Chandrasekharan MB, Wilson AJ, Zheng S, Yenamandra A, Locke K, Yuan J, Bonine-Summers AR, Wells CE, Kaiser JF, Washington MK, Zhao Z, Wagner FF, Sun ZW, Xa F, Holson EB, Khabele D, Hiebert SW. Hdac3 is essential for the maintenance of chromatin structure and genome stability. Cancer Cell. 2010;18:436–447. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Witt O, Deubzer HE, Milde T, Oehme I. HDAC family. what are the cancer relevant targets? Cancer Lett. 2009;277:8–21. - PubMed
-
- Jia H, Pallos J, Jacques V, Lau A, Tang B, Cooper A, Syed A, Purcell J, Chen Y, Sharma S, Sangrey GR, Darnell SB, Plasterer H, Sadri-Vakili G, Gottesfeld JM, Thompson LM, Rusche JR, Marsh JL, Thomas EA. Histone deacetylase (HDAC) inhibitors targeting HDAC3 and HDAC1 ameliorate polyglutamine-elicited phenotypes in model systems of Huntington's disease. Neurobiol Dis. 2012;46:351–361. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

