Muscle, skin and core temperature after -110°c cold air and 8°c water treatment
- PMID: 23139763
- PMCID: PMC3491015
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0048190
Muscle, skin and core temperature after -110°c cold air and 8°c water treatment
Abstract
The aim of this investigation was to elucidate the reductions in muscle, skin and core temperature following exposure to -110°C whole body cryotherapy (WBC), and compare these to 8°C cold water immersion (CWI). Twenty active male subjects were randomly assigned to a 4-min exposure of WBC or CWI. A minimum of 7 days later subjects were exposed to the other treatment. Muscle temperature in the right vastus lateralis (n=10); thigh skin (average, maximum and minimum) and rectal temperature (n=10) were recorded before and 60 min after treatment. The greatest reduction (P<0.05) in muscle (mean ± SD; 1 cm: WBC, 1.6 ± 1.2°C; CWI, 2.0 ± 1.0°C; 2 cm: WBC, 1.2 ± 0.7°C; CWI, 1.7 ± 0.9°C; 3 cm: WBC, 1.6 ± 0.6°C; CWI, 1.7 ± 0.5°C) and rectal temperature (WBC, 0.3 ± 0.2°C; CWI, 0.4 ± 0.2°C) were observed 60 min after treatment. The largest reductions in average (WBC, 12.1 ± 1.0°C; CWI, 8.4 ± 0.7°C), minimum (WBC, 13.2 ± 1.4°C; CWI, 8.7 ± 0.7°C) and maximum (WBC, 8.8 ± 2.0°C; CWI, 7.2 ± 1.9°C) skin temperature occurred immediately after both CWI and WBC (P<0.05). Skin temperature was significantly lower (P<0.05) immediately after WBC compared to CWI. The present study demonstrates that a single WBC exposure decreases muscle and core temperature to a similar level of those experienced after CWI. Although both treatments significantly reduced skin temperature, WBC elicited a greater decrease compared to CWI. These data may provide information to clinicians and researchers attempting to optimise WBC and CWI protocols in a clinical or sporting setting.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


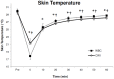
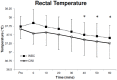
References
-
- Costello JT, Algar LA, Donnelly AE (2012) Effects of whole-body cryotherapy (−110°C) on proprioception and indices of muscle damage. Scand J Med Sci Sports 22(2): 190–198. - PubMed
-
- Hausswirth C, Louis J, Bieuzen F, Pournot H, Fournier J, et al. (2011) Effects of whole-body cryotherapy vs. far-Infrared vs. passive modalities on recovery from exercise-induced muscle damage in highly-trained runners. PLoS ONE 6(12): e227749 doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0027749. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Pournot H, Bieuzen F, Louis J, Mounier R, Fillard JR, et al. (2011) Time-course of changes in inflammatory response after whole-body cryotherapy multi exposures following severe exercise. PLoS One 6(7): e22748 doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0022748. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Banfi G, Lombardi G, Colombini A, Melegati G (2010) Whole-body cryotherapy in athletes. Sports Med 40(6): 509–517. - PubMed
-
- Enwemeka CS, Allen C, Avila P, Bina J, Kondrade J, et al. (2002) Soft tissue thermodynamics before, during, and after cold pack therapy. Med Sci Sports Exerc 34: 45–50. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

