Homocysteine induces apoptosis of rat hippocampal neurons by inhibiting 14-3-3ε expression and activating calcineurin
- PMID: 23139767
- PMCID: PMC3491063
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0048247
Homocysteine induces apoptosis of rat hippocampal neurons by inhibiting 14-3-3ε expression and activating calcineurin
Abstract
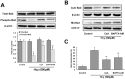
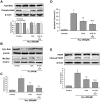
A high level of plasma homocysteine (Hcy) increases the risk for neurodegenerative diseases. One such disorder is Alzheimer's disease, which involves marked neuronal apoptosis of unknown etiology. This study shows that Hcy inhibits expression of 14-3-3ε and activates calcineurin in rat hippocampal neurons in a dose-dependent manner. Calcineurin-mediated Bad dephosphorylation, which is blocked by calcineurin inhibition and Ca(2+) chelation, causes mitochondrial translocation of Bad and apoptosis; this step in the apoptotic pathway is synergistically blocked by calcineurin inhibition and overexpression of 14-3-3ε. These findings demonstrated that calcineurin activation and downregulation of 14-3-3ε may be one of the mechanisms of Hcy-induced apoptosis of hippocampal neurons.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures




References
-
- Selhub J (1999) Homocysteine metabolism. Annu Rev Nutr 19: 217–246. - PubMed
-
- Biasioli S, Schiavon R (2000) Homocysteine as a Cardiovascular Risk Factor. Blood Purification 18: 177–182. - PubMed
-
- Joosten E, Lesaffre E, Riezler R, Ghekiere V, Dereymaeker L, et al. (1997) Is metabolic evidence for vitamin B-12 and folate deficiency more frequent in elderly patients with Alzheimer's disease? J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci 52: M76–79. - PubMed
-
- Sachdev P (2004) Homocysteine, cerebrovascular disease and brain atrophy. J Neurol Sci 226: 25–29. - PubMed
-
- Eto K, Asada T, Arima K, Makifuchi T, Kimura H (2002) Brain hydrogen sulfide is severely decreased in Alzheimer's disease. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 293: 1485–1488. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

