Role of C-terminal negative charges and tyrosine residues in fibril formation of α-synuclein
- PMID: 23139905
- PMCID: PMC3489812
- DOI: 10.1002/brb3.86
Role of C-terminal negative charges and tyrosine residues in fibril formation of α-synuclein
Abstract
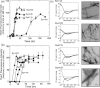
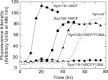
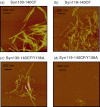
α-Synuclein (140 amino acids), one of the causative proteins of Parkinson's disease, forms amyloid fibrils in brain neuronal cells. In order to further explore the contributions of the C-terminal region of α-synuclein in fibril formation and also to understand the overall mechanism of fibril formation, we reduced the number of negatively charged residues in the C-terminal region using mutagenesis. Mutants with negative charges deleted displayed accelerated fibril formation compared with wild-type α-synuclein, demonstrating that negative charges located in the C-terminal region of α-synuclein modulate fibril formation. Additionally, when tyrosine residues located at position 125, 133, and 136 in the C-terminal region were changed to alanine residue(s), we found that all mutants containing the Tyr136Ala mutation showed delays in fibril formation compared with wild type. Mutation of Tyr136 to various amino acids revealed that aromatic residues located at this position act favorably toward fibril formation. In mutants where charge neutralization and tyrosine substitution were combined, we found that these two factors influence fibril formation in complex fashion. These findings highlight the importance of negative charges and aromatic side chains in the C-terminal region of α-synuclein in fibril formation.
Keywords: Amyloid; Parkinson's disease; amyloid formation mechanism; protein aggregation; site-directed mutagenesis; α-Synuclein.
Figures





References
-
- Bisaglia M, Mammi S, Bubacco L. Structural insights on physiological functions and pathological effects of alpha-synuclein. FASEB J. 2009;23:329–340. - PubMed
-
- Carrell RW, Lomas DA. Conformational disease. Lancet. 1997;350:134–138. - PubMed
-
- Conway KA, Harper JD, Lansbury PT., Jr Fibrils formed in vitro from alpha-synuclein and two mutant forms linked to Parkinson's disease are typical amyloid. Biochemistry. 2000;39:2552–2563. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

