MiR-15b and miR-152 reduce glioma cell invasion and angiogenesis via NRP-2 and MMP-3
- PMID: 23142217
- PMCID: PMC3553580
- DOI: 10.1016/j.canlet.2012.10.026
MiR-15b and miR-152 reduce glioma cell invasion and angiogenesis via NRP-2 and MMP-3
Abstract
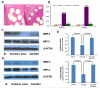
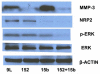
We tested invasion and angiogenesis related mRNA expression and miRNA profiles of glioma. Genes with mRNA expression that changed significantly were selected to predict possible miRNAs that regulate mRNA expression, and were then matched with miRNA results. NRP-2 with the matching miRNA miR-15b, and MMP-3 with the matching miRNA miR-152 were selected for further study. Luciferase activity assay confirmed that miR-15b and miR-152 attenuate expression of NRP-2 and MMP-3 protein by binding to NRP-2 and MMP-3 transcript, respectively. In vitro invasion assay data showed that miR-15b and miR-152 significantly decreased 9L cell invasiveness. In vitro tube formation assay data showed that miR-15b reduced tube formation. A preliminary pathway study indicated that miR-15b and miR-152 deactivated the MEK-ERK pathway via NRP-2 and MMP-3 in 9L cells, respectively.
Copyright © 2012 Elsevier Ireland Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures


References
-
- Nicholas MK, Prados MD, Larson DA, Black PM, Loeffler J. Malignant Astrocytomas in Cancer of the Nervous System. Blackwell Publishers; Oxford: 1997.
-
- Burger PC, Dubois PJ, Schold SC, Jr., Smith KR, Jr., Odom GL, Crafts DC, Giangaspero F. Computerized tomographic and pathologic studies of the untreated, quiescent, and recurrent glioblastoma multiforme. Journal of neurosurgery. 1983;58:159–169. - PubMed
-
- Daumas-Duport C, Scheithauer BW, Kelly PJ. A histologic and cytologic method for the spatial definition of gliomas. Mayo Clin Proc. 1987;62:435–449. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

