Phase I and clinical pharmacology study of bevacizumab, sorafenib, and low-dose cyclophosphamide in children and young adults with refractory/recurrent solid tumors
- PMID: 23143218
- PMCID: PMC3537913
- DOI: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-12-1897
Phase I and clinical pharmacology study of bevacizumab, sorafenib, and low-dose cyclophosphamide in children and young adults with refractory/recurrent solid tumors
Erratum in
- Clin Cancer Res. 2013 Apr 1;19(7):1914
Abstract
Purpose: To determine the maximum-tolerated dose (MTD), dose-limiting toxicities (DLT), pharmacokinetics, and pharmacodynamics of sorafenib, bevacizumab, and low-dose oral cyclophosphamide in children and young adults with recurrent/refractory solid tumors.
Experimental design: Sorafenib dose was escalated from 90 to 110 mg/m(2) twice daily with fixed doses of bevacizumab at 5 mg/kg every 3 weeks and cyclophosphamide at 50 mg/m(2) daily. Once sorafenib's MTD was established, bevacizumab dose was escalated. Each course was of 21 days. Pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics studies were conducted during the first course.
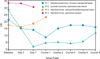
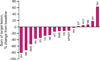
Results: Nineteen patients (11 males; median age, 9.2 years) received a median of four courses (range, 1-23). DLTs during course 1 included grade 3 rash (two), increased lipase (one), anorexia (one), and thrombus (one). With an additional 71 courses of therapy, the most common toxicities ≥ grade 3 included neutropenia (nine), lymphopenia (nine), and rashes (four). Five of 17 evaluable patients had partial tumor responses, and five had disease stabilization (>2 courses). Median day 1 cyclophosphamide apparent oral clearance was 3.13 L/h/m(2). Median day 1 sorafenib apparent oral clearance was 44 and 39 mL/min/m(2) at the 2 dose levels evaluated, and steady-state concentrations ranged from 1.64 to 4.8 mg/L. Inhibition of serum VEGF receptor 2 (VEGFR2) was inversely correlated with sorafenib steady-state concentrations (P = 0.019).
Conclusion: The recommended phase II doses are sorafenib, 90 mg/m(2) twice daily; bevacizumab, 15 mg/kg q3 weeks; and cyclophosphamide, 50 mg/m(2) once daily. This regimen is feasible with promising evidence of antitumor activity that warrants further investigation.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Phase I expansion cohort to evaluate the combination of bevacizumab, sorafenib and low-dose cyclophosphamide in children and young adults with refractory or recurrent solid tumours.Eur J Cancer. 2020 Jun;132:35-42. doi: 10.1016/j.ejca.2020.03.010. Epub 2020 Apr 20. Eur J Cancer. 2020. PMID: 32325418 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Combination targeted therapy with sorafenib and bevacizumab results in enhanced toxicity and antitumor activity.J Clin Oncol. 2008 Aug 1;26(22):3709-14. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2007.10.8332. J Clin Oncol. 2008. PMID: 18669456 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Dual antiangiogenic inhibition: a phase I dose escalation and expansion trial targeting VEGF-A and VEGFR in patients with advanced solid tumors.Invest New Drugs. 2015 Feb;33(1):215-24. doi: 10.1007/s10637-014-0176-4. Epub 2014 Nov 4. Invest New Drugs. 2015. PMID: 25363205 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
A phase I trial and pharmacokinetic study of sorafenib in children with refractory solid tumors or leukemias: a Children's Oncology Group Phase I Consortium report.Clin Cancer Res. 2012 Nov 1;18(21):6011-22. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-11-3284. Epub 2012 Sep 7. Clin Cancer Res. 2012. PMID: 22962440 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Phase I pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic study of lapatinib in combination with sorafenib in patients with advanced refractory solid tumors.Eur J Cancer. 2013 Mar;49(5):989-98. doi: 10.1016/j.ejca.2012.10.016. Epub 2012 Nov 9. Eur J Cancer. 2013. PMID: 23146956 Clinical Trial.
Cited by
-
A phase 1 trial of everolimus and bevacizumab in children with recurrent solid tumors.Cancer. 2020 Apr 15;126(8):1749-1757. doi: 10.1002/cncr.32722. Epub 2020 Jan 22. Cancer. 2020. PMID: 31967673 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Alternative formulations of sorafenib for use in children.Pediatr Blood Cancer. 2013 Oct;60(10):1642-6. doi: 10.1002/pbc.24619. Epub 2013 Jun 20. Pediatr Blood Cancer. 2013. PMID: 23788485 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Can Fluorine-18-Fluorodeoxyglucose Positron Emission Tomography Be Used As a Useful Method to Evaluate the Treatment Response to Neoadjuvant Therapy Combined With Sorafenib and Anti-VEGF in Children Diagnosed With Metastatical Bone Sarcoma?Iran J Pediatr. 2016 Mar 5;26(2):e4008. doi: 10.5812/ijp.4008. eCollection 2016 Apr. Iran J Pediatr. 2016. PMID: 27307968 Free PMC article.
-
Randomized Phase II Trial of Bevacizumab or Temsirolimus in Combination With Chemotherapy for First Relapse Rhabdomyosarcoma: A Report From the Children's Oncology Group.J Clin Oncol. 2019 Nov 1;37(31):2866-2874. doi: 10.1200/JCO.19.00576. Epub 2019 Sep 12. J Clin Oncol. 2019. PMID: 31513481 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Rationale for the use of tyrosine kinase inhibitors in the treatment of paediatric desmoid-type fibromatosis.Br J Cancer. 2021 May;124(10):1637-1646. doi: 10.1038/s41416-021-01320-1. Epub 2021 Mar 15. Br J Cancer. 2021. PMID: 33723397 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Pietras K, Hanahan D. A multitargeted, metronomic, and maximum-tolerated dose "chemo-switch" regimen is antiangiogenic, producing objective responses and survival benefit in a mouse model of cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2005;23:939–952. - PubMed
-
- Huang S, Armstrong EA, Benavente S, Chinnaiyan P, Harari PM. Dual-agent molecular targeting of the epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR): combining anti-EGFR antibody with tyrosine kinase inhibitor. Cancer Res. 2004;64:5355–5362. - PubMed
-
- Matar P, Rojo F, Cassia R, Moreno-Bueno G, Di Cosimo S, Tabernero J, et al. Combined epidermal growth factor receptor targeting with the tyrosine kinase inhibitor gefitinib (ZD1839) and the monoclonal antibody cetuximab (IMC-C225): superiority over single-agent receptor targeting. Clin Cancer Res. 2004;10:6487–6501. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

