Unravelling the enigma of selective vulnerability in neurodegeneration: motor neurons resistant to degeneration in ALS show distinct gene expression characteristics and decreased susceptibility to excitotoxicity
- PMID: 23143228
- PMCID: PMC3535376
- DOI: 10.1007/s00401-012-1058-5
Unravelling the enigma of selective vulnerability in neurodegeneration: motor neurons resistant to degeneration in ALS show distinct gene expression characteristics and decreased susceptibility to excitotoxicity
Abstract
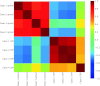
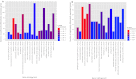
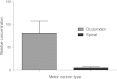
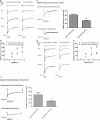
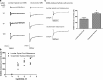
A consistent clinical feature of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) is the sparing of eye movements and the function of external sphincters, with corresponding preservation of motor neurons in the brainstem oculomotor nuclei, and of Onuf's nucleus in the sacral spinal cord. Studying the differences in properties of neurons that are vulnerable and resistant to the disease process in ALS may provide insights into the mechanisms of neuronal degeneration, and identify targets for therapeutic manipulation. We used microarray analysis to determine the differences in gene expression between oculomotor and spinal motor neurons, isolated by laser capture microdissection from the midbrain and spinal cord of neurologically normal human controls. We compared these to transcriptional profiles of oculomotor nuclei and spinal cord from rat and mouse, obtained from the GEO omnibus database. We show that oculomotor neurons have a distinct transcriptional profile, with significant differential expression of 1,757 named genes (q < 0.001). Differentially expressed genes are enriched for the functional categories of synaptic transmission, ubiquitin-dependent proteolysis, mitochondrial function, transcriptional regulation, immune system functions, and the extracellular matrix. Marked differences are seen, across the three species, in genes with a function in synaptic transmission, including several glutamate and GABA receptor subunits. Using patch clamp recording in acute spinal and brainstem slices, we show that resistant oculomotor neurons show a reduced AMPA-mediated inward calcium current, and a higher GABA-mediated chloride current, than vulnerable spinal motor neurons. The findings suggest that reduced susceptibility to excitotoxicity, mediated in part through enhanced GABAergic transmission, is an important determinant of the relative resistance of oculomotor neurons to degeneration in ALS.
Figures
References
-
- Ashburner M, Ball CA, Blake JA, Botstein D, Butler H, Cherry JM, Davis AP, Dolinski K, Dwight SS, Eppig JT, Harris MA, Hill DP, Issel-Tarver L, Kasarskis A, Lewis S, Matese JC, Richardson JE, Ringwald M, Rubin GM, Sherlock G. Gene ontology: tool for the unification of biology. The Gene Ontology Consortium. Nat Genet. 2000;25(1):25–29. doi: 10.1038/75556. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Davidson D, Graham E, Sime C, Hill R. A gene with sequence similarity to Drosophila engrailed is expressed during the development of the neural tube and vertebrae in the mouse. Development. 1988;104(2):305–316. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

