A dynamic and intricate regulatory network determines Pseudomonas aeruginosa virulence
- PMID: 23143271
- PMCID: PMC3592444
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gks1039
A dynamic and intricate regulatory network determines Pseudomonas aeruginosa virulence
Abstract
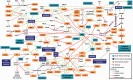
Pseudomonas aeruginosa is a metabolically versatile bacterium that is found in a wide range of biotic and abiotic habitats. It is a major human opportunistic pathogen causing numerous acute and chronic infections. The critical traits contributing to the pathogenic potential of P. aeruginosa are the production of a myriad of virulence factors, formation of biofilms and antibiotic resistance. Expression of these traits is under stringent regulation, and it responds to largely unidentified environmental signals. This review is focused on providing a global picture of virulence gene regulation in P. aeruginosa. In addition to key regulatory pathways that control the transition from acute to chronic infection phenotypes, some regulators have been identified that modulate multiple virulence mechanisms. Despite of a propensity for chaotic behaviour, no chaotic motifs were readily observed in the P. aeruginosa virulence regulatory network. Having a 'birds-eye' view of the regulatory cascades provides the forum opportunities to pose questions, formulate hypotheses and evaluate theories in elucidating P. aeruginosa pathogenesis. Understanding the mechanisms involved in making P. aeruginosa a successful pathogen is essential in helping devise control strategies.
Figures
References
-
- Mahajan-Miklos S, Rahme LG, Ausubel FM. Elucidating the molecular mechanisms of bacterial virulence using non-mammalian hosts. Mol. Microbiol. 2000;37:981–988. - PubMed
-
- Kerr KG, Snelling AM. Pseudomonas aeruginosa: a formidable and ever-present adversary. J. Hosp. Infect. 2009;73:338–344. - PubMed
-
- Valderrey AD, Pozuelo MJ, Jimenez PA, Macia MD, Oliver A, Rotger R. Chronic colonization by Pseudomonas aeruginosa of patients with obstructive lung diseases: cystic fibrosis, bronchiectasis, and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Diagn. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2010;68:20–27. - PubMed
-
- Bouza E, Burillo A, Munoz P. Catheter-related infections: diagnosis and intravascular treatment. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2002;8:265–274. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

