Genome-wide association analysis identifies new lung cancer susceptibility loci in never-smoking women in Asia
- PMID: 23143601
- PMCID: PMC4169232
- DOI: 10.1038/ng.2456
Genome-wide association analysis identifies new lung cancer susceptibility loci in never-smoking women in Asia
Abstract
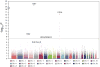
To identify common genetic variants that contribute to lung cancer susceptibility, we conducted a multistage genome-wide association study of lung cancer in Asian women who never smoked. We scanned 5,510 never-smoking female lung cancer cases and 4,544 controls drawn from 14 studies from mainland China, South Korea, Japan, Singapore, Taiwan and Hong Kong. We genotyped the most promising variants (associated at P < 5 × 10(-6)) in an additional 1,099 cases and 2,913 controls. We identified three new susceptibility loci at 10q25.2 (rs7086803, P = 3.54 × 10(-18)), 6q22.2 (rs9387478, P = 4.14 × 10(-10)) and 6p21.32 (rs2395185, P = 9.51 × 10(-9)). We also confirmed associations reported for loci at 5p15.33 and 3q28 and a recently reported finding at 17q24.3. We observed no evidence of association for lung cancer at 15q25 in never-smoking women in Asia, providing strong evidence that this locus is not associated with lung cancer independent of smoking.
Figures



References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

