Photoluminescent DNA binding and cytotoxic activity of a platinum(II) complex bearing a tetradentate β-diketiminate ligand
- PMID: 23143731
- PMCID: PMC3566370
- DOI: 10.1039/c2dt32462h
Photoluminescent DNA binding and cytotoxic activity of a platinum(II) complex bearing a tetradentate β-diketiminate ligand
Abstract
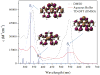
A platinum(II) complex of a monoanionic, tetradentate β-diketiminate (BDI) ligand with pendant quinoline arms, BDI(QQ)H, is reported. The complex, [Pt(BDI(QQ))]Cl, is emissive in DMSO, but non-emissive in aqueous buffer. Upon binding DNA in buffer, however, a 150-fold turn-on in emission intensity occurs. Dynamic light scattering and (1)H NMR spectroscopy indicate that [Pt(BDI(QQ))]Cl forms non-emissive aggregates in aqueous solution; DNA-binding disperses the aggregates leading to the large emission turn-on response. The cytotoxic activity of the complex, measured in two cancer cell lines, is comparable to or better than that of the established anticancer drug cisplatin.
Figures


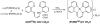
References
-
- Bailey JA, Hill MG, Marsh RE, Miskowski VM, Schaefer WP, Gray HB. Inorg Chem. 1995;34:4591.
-
- Connick WB, Henling LM, Marsh RE, Gray HB. Inorg Chem. 1996;35:6261.
-
- Lai SW, Che CM. Top Curr Chem. 2004;241:27.
-
- Howe-Grant M, Wu KC, Bauer WR, Lippard SJ. Biochemistry. 1976;15:4339. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

