Mai infection simulating metastatic breast cancer
- PMID: 23144339
- PMCID: PMC4542980
- DOI: 10.1136/bcr-01-2012-5640
Mai infection simulating metastatic breast cancer
Abstract
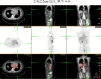
We represent a case of an asymptomatic female who was found to have a mass in the right breast which confirmed an invasive ductal carcinoma by core biopsy. After 3 months of completion of chemo-radiotherapy, the patient remained totally asymptomatic. However, positron emission tomography scan showed four hypermetabolic lesions in the left lung thought to be consistent with metastatic disease. Standard uptake value ranged between 3.86 and 6; the results were consistent with metastatic breast cancer, so wedge resection was performed. Caseating granulomatous inflammation with necrosis was reported. Ultimately culture revealed Mycobacterium avium intracellulare infection. The lesions resolved completely after a course of antibiotics.
Figures

References
-
- Tsunezuka Y, Ishikawa N, Hiranuma C, et al. Mycobacteria other than tuberculosis combined primary lung cancer. Kyobu Geka 2004;57:119–22. - PubMed
-
- Kobashi Y, Yoshida K, Miyashita N, et al. Pulmonary Mycobacterium avium disease with a solitary pulmonary nodule requiring differentiation from recurrence of pulmonary adenocarcinoma. Intern Med 2004;43:855–60. - PubMed
-
- Kobashi Y, Yoshida K, Miyashita N, et al. A case of pulmonary Mycobacterium intracellulare infectious disease with a solitary pulmonary nodule in the peripheral lung field. Nihon Kokyuki Gakkai Zasshi 2004;42:831–6. - PubMed
-
- Suzuki K, Hashimoto T, Tanaka E, et al. A case of Mycobacterium avium disease presenting as a solitary pulmonary nodule and resected under a suspicion of lung cancer. Kekkaku 1995;70:25–9. - PubMed
-
- Nakamura Y, Okada Y, Endo C, et al. Endobronchial carcinoid tumor combined with pulmonary non-tuberculous mycobacterial infection: report of two cases. Lung Cancer 2003;39:227–9. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
