Conjugated linoleic acid is a preferential substrate for fatty acid nitration
- PMID: 23144452
- PMCID: PMC3531723
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M112.401356
Conjugated linoleic acid is a preferential substrate for fatty acid nitration
Abstract
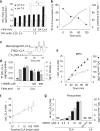
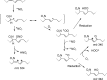
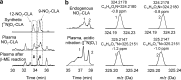
The oxidation and nitration of unsaturated fatty acids by oxides of nitrogen yield electrophilic derivatives that can modulate protein function via post-translational protein modifications. The biological mechanisms accounting for fatty acid nitration and the specific structural characteristics of products remain to be defined. Herein, conjugated linoleic acid (CLA) is identified as the primary endogenous substrate for fatty acid nitration in vitro and in vivo, yielding up to 10(5) greater extent of nitration products as compared with bis-allylic linoleic acid. Multiple enzymatic and cellular mechanisms account for CLA nitration, including reactions catalyzed by mitochondria, activated macrophages, and gastric acidification. Nitroalkene derivatives of CLA and their metabolites are detected in the plasma of healthy humans and are increased in tissues undergoing episodes of ischemia reperfusion. Dietary CLA and nitrite supplementation in rodents elevates NO(2)-CLA levels in plasma, urine, and tissues, which in turn induces heme oxygenase-1 (HO-1) expression in the colonic epithelium. These results affirm that metabolic and inflammatory reactions yield electrophilic products that can modulate adaptive cell signaling mechanisms.
Figures




References
-
- Saravanan P., Davidson N. C., Schmidt E. B., Calder P. C. (2010) Cardiovascular effects of marine ω-3 fatty acids. Lancet 376, 540–550 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01 HL132550/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R00 HL095769/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U54 GM103529/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- P01-HL103455/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P30-DK072506/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P01 HL103455/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01-HL058115/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL058115/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AT006822-01/AT/NCCIH NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK072506/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AT006822/AT/NCCIH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL064937/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01-HL64937/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- K99 HL095769/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

