Recurrence of dislocation following total hip arthroplasty revision using dual mobility cups was rare in 180 hips followed over 7 years
- PMID: 23144637
- PMCID: PMC3470678
- DOI: 10.1007/s11420-012-9301-0
Recurrence of dislocation following total hip arthroplasty revision using dual mobility cups was rare in 180 hips followed over 7 years
Abstract
Background: Dual mobility (DM) cups of mobile polyethylene were introduced to prevent total hip arthroplasty (THA) dislocation, but no large series with this design to treat recurrent instability have been reported.
Purpose: Our retrospective investigation ascertained the efficiency of DM cups in correction of recurrent dislocation and assessed any adverse effects.
Methods: One hundred eighty THAs with recurrent instability were revised to DM cups in 180 patients (mean age, 67.4 ± 11.7 years; range, 19 to 92 years). Thirty-one patients (17.2%) underwent at least one earlier THA revision, and 15 (10.3%) incurred non-union of the greater trochanter. Of the initial group in 2009, 145 patients had completed evaluations which included assessment of the Harris Hip Score and a radiographic assessment at a mean follow-up of 7.7 ± 2.2 years (range, 4 to 14 years). The rate of survival was calculated considering any reason for revision as failure.
Results: At follow-up, Harris hip score was 83.9 ± 16.1 (range, 21 to 100). Dislocation of the large articulation occurred in seven hips (4.8%), and only two recurred (1.4%) (one requiring additional revision). In addition, two intra-prosthetic dislocations of the small articulation (1.4%) were observed and needed revision surgery. The large number of earlier surgeries and non-union of the greater trochanter were related to recurrent instability. Two cups (1.4%) showed signs of definite loosening; six (4.1%) presented signs of possible loosening. Twenty-nine hips manifested femoral or acetabular osteolysis (20%), but only three were severe. Eight-year survival rate considering revision for any reason was 92.6% (95% CI, 85.5-96.4%).
Conclusions: This series indicates that DM cups are a viable option to treat recurrent THA instability. Their design provides a low risk of recurrent instability without increasing mechanical complications.
Keywords: bearing; dual mobility; hip arthroplasty; instability; polyethylene; revision; wear.
Figures

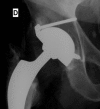
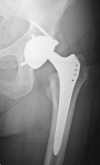
Similar articles
-
Use of dual mobility cup cemented into a tantalum acetabular shell for hip revision with large bone loss can decrease dislocation risk without increasing the risk of mechanical failure.Orthop Traumatol Surg Res. 2024 Apr;110(2):103739. doi: 10.1016/j.otsr.2023.103739. Epub 2023 Oct 31. Orthop Traumatol Surg Res. 2024. PMID: 37918693
-
Low rate of dislocation of dual-mobility cups in primary total hip arthroplasty.Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2013 Dec;471(12):3891-900. doi: 10.1007/s11999-013-2929-3. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2013. PMID: 23516032 Free PMC article.
-
Is Isolated Mobile Component Exchange an Option in the Management of Intraprosthetic Dislocation of a Dual Mobility Cup?Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2020 Feb;478(2):279-287. doi: 10.1097/CORR.0000000000001055. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2020. PMID: 31794492 Free PMC article.
-
Risk factors and modes of failure in the modern dual mobility implant. A systematic review and meta-analysis.BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2021 Jun 14;22(1):541. doi: 10.1186/s12891-021-04404-4. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2021. PMID: 34126990 Free PMC article.
-
Modular dual mobility cups with multihole metal back in total hip arthroplasty revision: a systematic review.J Biol Regul Homeost Agents. 2019 Mar-Apr;33(2 Suppl. 1):63-67. XIX Congresso Nazionale S.I.C.O.O.P. Societa' Italiana Chirurghi Ortopedici Dell'ospedalita' Privata Accreditata. J Biol Regul Homeost Agents. 2019. PMID: 31169005
Cited by
-
Dual mobility for total hip arthroplasty revision surgery: A systematic review and metanalysis.SICOT J. 2021;7:18. doi: 10.1051/sicotj/2021015. Epub 2021 Mar 22. SICOT J. 2021. PMID: 33749588 Free PMC article.
-
Five to thirteen year results of a cemented dual mobility socket to treat recurrent dislocation.Int Orthop. 2017 Mar;41(3):513-519. doi: 10.1007/s00264-016-3343-8. Epub 2016 Nov 26. Int Orthop. 2017. PMID: 27889840
-
Comparison of Constrained Acetabular Components and Dual Mobility Cups in Revision Total Hip Arthroplasty: A Literature Review.Hip Pelvis. 2020 Jun;32(2):59-69. doi: 10.5371/hp.2020.32.2.59. Epub 2020 Jun 15. Hip Pelvis. 2020. PMID: 32566536 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Otto Aufranc Award: Dual-mobility Constructs in Revision THA Reduced Dislocation, Rerevision, and Reoperation Compared With Large Femoral Heads.Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2018 Feb;476(2):293-301. doi: 10.1007/s11999.0000000000000035. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2018. PMID: 29529658 Free PMC article.
-
Dual mobility cups in revision total hip arthroplasty.Int Orthop. 2017 Mar;41(3):535-542. doi: 10.1007/s00264-016-3363-4. Epub 2016 Dec 8. Int Orthop. 2017. PMID: 27933422
References
-
- Beaulé PE, Roussignol X, Schmalzried TP, Udomkiat P, Amstutz HC, Dujardin FH. Tripolar arthroplasty for recurrent total hip prosthesis dislocation. Rev. Chir. Orthop. Reparatrice Appar. Mot. 2003;89:242–249. - PubMed
-
- Berend KR, Lombardi AV, Jr, Mallory TH, Adams JB, Russell JH, Groseth KL. The long-term outcome of 755 consecutive constrained acetabular components in total hip arthroplasty examining the successes and failures. J. Arthroplasty. 2005;20(7 Suppl 3):93–102. doi: 10.1016/j.arth.2005.06.001. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

