Urea amidolyase (DUR1,2) contributes to virulence and kidney pathogenesis of Candida albicans
- PMID: 23144764
- PMCID: PMC3483220
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0048475
Urea amidolyase (DUR1,2) contributes to virulence and kidney pathogenesis of Candida albicans
Abstract
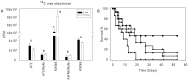
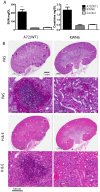
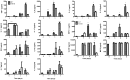
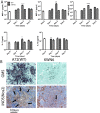
The intracellular enzyme urea amidolyase (Dur1,2p) enables C. albicans to utilize urea as a sole nitrogen source. Because deletion of the DUR1,2 gene reduces survival of C. albicans co-cultured with a murine macrophage cell line, we investigated the role of Dur1,2p in pathogenesis using a mouse model of disseminated candidiasis. A dur1,2Δ/dur1,2Δ strain was significantly less virulent than the wild-type strain, showing significantly higher survival rate, better renal function, and decreased and less sustained fungal colonization in kidney and brain. Complementation of the mutant restored virulence. DUR1,2 deletion resulted in a milder host inflammatory reaction. Immunohistochemistry, flow cytometry, and magnetic resonance imaging showed decreased phagocytic infiltration into infected kidneys. Systemic cytokine levels of wild-type mice infected with the dur1,2 mutant showed a more balanced systemic pro-inflammatory cytokine response. Host gene expression and protein analysis in infected kidneys revealed parallel changes in the local immune response. Significant differences were observed in the kidney IL-1 inflammatory pathway, IL-15 signaling, MAP kinase signaling, and the alternative complement pathway. We conclude that Dur1,2p is important for kidney colonization during disseminated candidiasis and contributes to an unbalanced host inflammatory response and subsequent renal failure. Therefore, this Candida-specific enzyme may represent a useful drug target to protect the host from kidney damage associated with disseminated candidiasis.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


Similar articles
-
Dur3 is the major urea transporter in Candida albicans and is co-regulated with the urea amidolyase Dur1,2.Microbiology (Reading). 2011 Jan;157(Pt 1):270-279. doi: 10.1099/mic.0.045005-0. Epub 2010 Sep 30. Microbiology (Reading). 2011. PMID: 20884691 Free PMC article.
-
Arginine-induced germ tube formation in Candida albicans is essential for escape from murine macrophage line RAW 264.7.Infect Immun. 2009 Apr;77(4):1596-605. doi: 10.1128/IAI.01452-08. Epub 2009 Feb 2. Infect Immun. 2009. PMID: 19188358 Free PMC article.
-
Glutamate dehydrogenase (Gdh2)-dependent alkalization is dispensable for escape from macrophages and virulence of Candida albicans.PLoS Pathog. 2020 Sep 16;16(9):e1008328. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1008328. eCollection 2020 Sep. PLoS Pathog. 2020. PMID: 32936835 Free PMC article.
-
The role of IL-33 in host response to Candida albicans.ScientificWorldJournal. 2014;2014:340690. doi: 10.1155/2014/340690. Epub 2014 Jul 21. ScientificWorldJournal. 2014. PMID: 25136658 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Host targets of candidalysin.PLoS Pathog. 2025 Jun 23;21(6):e1013284. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1013284. eCollection 2025 Jun. PLoS Pathog. 2025. PMID: 40549807 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The urea carboxylase and allophanate hydrolase activities of urea amidolyase are functionally independent.Protein Sci. 2016 Oct;25(10):1812-24. doi: 10.1002/pro.2990. Epub 2016 Aug 5. Protein Sci. 2016. PMID: 27452902 Free PMC article.
-
Landscape of gene expression variation of natural isolates of Cryptococcus neoformans in response to biologically relevant stresses.Microb Genom. 2020 Jan;6(1):e000319. doi: 10.1099/mgen.0.000319. Microb Genom. 2020. PMID: 31860441 Free PMC article.
-
Endothelial nitric oxide synthase limits host immunity to control disseminated Candida albicans infections in mice.PLoS One. 2019 Oct 31;14(10):e0223919. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0223919. eCollection 2019. PLoS One. 2019. PMID: 31671151 Free PMC article.
-
First Report of Pathogenic Bacterium Kalamiella piersonii Isolated from Urine of a Kidney Stone Patient: Draft Genome and Evidence for Role in Struvite Crystallization.Pathogens. 2020 Aug 29;9(9):711. doi: 10.3390/pathogens9090711. Pathogens. 2020. PMID: 32872396 Free PMC article.
-
Anuria in a solitary kidney with Candida bezoars managed conservatively.Eur J Pediatr. 2014 Dec;173(12):1623-5. doi: 10.1007/s00431-013-2201-6. Epub 2013 Nov 9. Eur J Pediatr. 2014. PMID: 24213483
References
-
- Vincent JL, Norrenberg M (2009) Intensive care unit-acquired weakness: framing the topic. Crit Care Med 37: S296–298. - PubMed
-
- Trick WE, Fridkin SK, Edwards JR, Hajjeh RA, Gaynes RP (2002) Secular trend of hospital-acquired candidemia among intensive care unit patients in the United States during 1989–1999. Clin Infect Dis 35: 627–630. - PubMed
-
- Calderone AR, Clancy JC, editors (2012) Candida and candidiasis. 2 ed: Amer Society for Microbiology. 534 p.
-
- Odds FC (1988) Candida and candidiasis. London: Bailliere Tindall.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

