O:2-CRM(197) conjugates against Salmonella Paratyphi A
- PMID: 23144798
- PMCID: PMC3492368
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0047039
O:2-CRM(197) conjugates against Salmonella Paratyphi A
Abstract
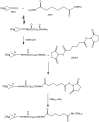
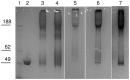
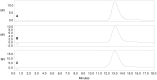
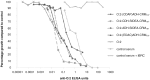
Enteric fevers remain a common and serious disease, affecting mainly children and adolescents in developing countries. Salmonella enterica serovar Typhi was believed to cause most enteric fever episodes, but several recent reports have shown an increasing incidence of S. Paratyphi A, encouraging the development of a bivalent vaccine to protect against both serovars, especially considering that at present there is no vaccine against S. Paratyphi A. The O-specific polysaccharide (O:2) of S. Paratyphi A is a protective antigen and clinical data have previously demonstrated the potential of using O:2 conjugate vaccines. Here we describe a new conjugation chemistry to link O:2 and the carrier protein CRM(197), using the terminus 3-deoxy-D-manno-octulosonic acid (KDO), thus leaving the O:2 chain unmodified. The new conjugates were tested in mice and compared with other O:2-antigen conjugates, synthesized adopting previously described methods that use CRM(197) as carrier protein. The newly developed conjugation chemistry yielded immunogenic conjugates with strong serum bactericidal activity against S. Paratyphi A.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures






References
-
- Bodhidatta L, Taylor DN, Thisyakorn U, Echeverria P (1987) Control of typhoid fever in Bangkok, Thailand, by annual immunization of schoolchildren with parenteral typhoid vaccine. Rev Infect Dis 9: 841–845. - PubMed
-
- Podda A, Saul AJ, Arora R, Bhutta Z, Sinha A, et al. (2010) Conjugate vaccines for enteric fever: proceedings of a meeting organized in New Delhi, India in 2009. J Infect Dev Ctries 4: 404–411. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

