Is wetter better? An evaluation of over-the-counter personal lubricants for safety and anti-HIV-1 activity
- PMID: 23144863
- PMCID: PMC3492332
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0048328
Is wetter better? An evaluation of over-the-counter personal lubricants for safety and anti-HIV-1 activity
Abstract
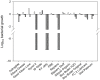
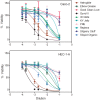
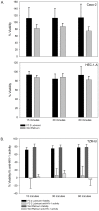
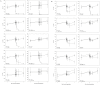
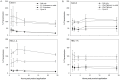
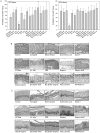
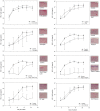
Because lubricants may decrease trauma during coitus, it is hypothesized that they could aid in the prevention of HIV acquisition. Therefore, safety and anti-HIV-1 activity of over-the-counter (OTC) aqueous- (n = 10), lipid- (n = 2), and silicone-based (n = 2) products were tested. The rheological properties of the lipid-based lubricants precluded testing with the exception of explant safety testing. Six aqueous-based gels were hyperosmolar, two were nearly iso-osmolar, and two were hypo-osmolar. Evaluation of the panel of products showed Gynol II (a spermicidal gel containing 2% nonoxynol-9), KY Jelly, and Replens were toxic to Lactobacillus. Two nearly iso-osmolar aqueous- and both silicone-based gels were not toxic toward epithelial cell lines or ectocervical or colorectal explant tissues. Hyperosmolar lubricants demonstrated reduction of tissue viability and epithelial fracture/sloughing while the nearly iso-osmolar and silicon-based lubricants showed no significant changes in tissue viability or epithelial modifications. While most of the lubricants had no measurable anti-HIV-1 activity, three lubricants which retained cell viability did demonstrate modest anti-HIV-1 activity in vitro. To determine if this would result in protection of mucosal tissue or conversely determine if the epithelial damage associated with the hyperosmolar lubricants increased HIV-1 infection ex vivo, ectocervical tissue was exposed to selected lubricants and then challenged with HIV-1. None of the lubricants that had a moderate to high therapeutic index protected the mucosal tissue. These results show hyperosmolar lubricant gels were associated with cellular toxicity and epithelial damage while showing no anti-viral activity. The two iso-osmolar lubricants, Good Clean Love and PRÉ, and both silicone-based lubricants, Female Condom 2 lubricant and Wet Platinum, were the safest in our testing algorithm.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Tanner AE, Zimet G, Fortenberry JD, Reece M, Graham C, et al. (2009) Young women’s use of a vaginal microbicide surrogate: the role of individual and contextual factors in acceptability and sexual pleasure. J Sex Res 46: 15–23. - PubMed
-
- El-Sadr WM, Mayer KH, Maslankowski L, Hoesley C, Justman J, et al. (2006) Safety and acceptability of cellulose sulfate as a vaginal microbicide in HIV-infected women. AIDS 20: 1109–1116. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

