DNA repair and cell cycle biomarkers of radiation exposure and inflammation stress in human blood
- PMID: 23144912
- PMCID: PMC3492462
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0048619
DNA repair and cell cycle biomarkers of radiation exposure and inflammation stress in human blood
Abstract
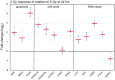
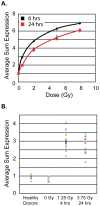
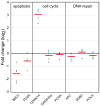
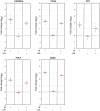
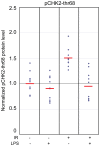
DNA damage and repair are hallmarks of cellular responses to ionizing radiation. We hypothesized that monitoring the expression of DNA repair-associated genes would enhance the detection of individuals exposed to radiation versus other forms of physiological stress. We employed the human blood ex vivo radiation model to investigate the expression responses of DNA repair genes in repeated blood samples from healthy, non-smoking men and women exposed to 2 Gy of X-rays in the context of inflammation stress mimicked by the bacterial endotoxin lipopolysaccharide (LPS). Radiation exposure significantly modulated the transcript expression of 12 genes of 40 tested (2.2E-06<p<0.03), of which 8 showed no overlap between unirradiated and irradiated samples (CDKN1A, FDXR, BBC3, PCNA, GADD45a, XPC, POLH and DDB2). This panel demonstrated excellent dose response discrimination (0.5 to 8 Gy) in an independent human blood ex vivo dataset, and 100% accuracy for discriminating patients who received total body radiation. Three genes of this panel (CDKN1A, FDXR and BBC3) were also highly sensitive to LPS treatment in the absence of radiation exposure, and LPS co-treatment significantly affected their radiation responses. At the protein level, BAX and pCHK2-thr68 were elevated after radiation exposure, but the pCHK2-thr68 response was significantly decreased in the presence of LPS. Our combined panel yields an estimated 4-group accuracy of ∼90% to discriminate between radiation alone, inflammation alone, or combined exposures. Our findings suggest that DNA repair gene expression may be helpful to identify biodosimeters of exposure to radiation, especially within high-complexity exposure scenarios.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


Similar articles
-
Developing Gender-Specific Gene Expression Biodosimetry Using a Panel of Radiation-Responsive Genes for Determining Radiation Dose in Human Peripheral Blood.Radiat Res. 2019 Aug;192(4):399-409. doi: 10.1667/RR15355.1. Epub 2019 Aug 2. Radiat Res. 2019. PMID: 31373872
-
Identification of Differential Gene Expression Patterns after Acute Exposure to High and Low Doses of Low-LET Ionizing Radiation in a Reconstituted Human Skin Tissue.Radiat Res. 2016 Nov;186(5):531-538. doi: 10.1667/RR14471.1. Epub 2016 Nov 1. Radiat Res. 2016. PMID: 27802111
-
Identification of potential mRNA biomarkers in peripheral blood lymphocytes for human exposure to ionizing radiation.Radiat Res. 2000 Sep;154(3):342-6. doi: 10.1667/0033-7587(2000)154[0342:iopmbi]2.0.co;2. Radiat Res. 2000. PMID: 11012342
-
Candidate gene biodosimeters of mice and human exposure to ionizing radiation by quantitative reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction.J Cancer Res Ther. 2015 Jul-Sep;11(3):549-57. doi: 10.4103/0973-1482.160912. J Cancer Res Ther. 2015. PMID: 26458580 Review.
-
Stress, inflammation, and defense of homeostasis.Mol Cell. 2014 Apr 24;54(2):281-8. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2014.03.030. Mol Cell. 2014. PMID: 24766892 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Ionising radiation exposure-induced regulation of selected biomarkers and their impact in cancer and treatment.Front Nucl Med. 2024 Oct 21;4:1469897. doi: 10.3389/fnume.2024.1469897. eCollection 2024. Front Nucl Med. 2024. PMID: 39498386 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Epigenetic Modulation of Inflammatory Pathways in Myometrial Stem Cells and Risk of Uterine Fibroids.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Jul 19;24(14):11641. doi: 10.3390/ijms241411641. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37511399 Free PMC article.
-
Enhanced γ-H2AX Foci Frequency and Altered Gene Expression in Participants Exposed to Ionizing Radiation During I-131 Nuclear Medicine Procedures.Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2024 Oct;58(6):341-353. doi: 10.1007/s13139-024-00872-3. Epub 2024 Jul 12. Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2024. PMID: 39308490
-
Transcript Analysis for Internal Biodosimetry Using Peripheral Blood from Neuroblastoma Patients Treated with (131)I-mIBG, a Targeted Radionuclide.Radiat Res. 2016 Sep;186(3):235-44. doi: 10.1667/RR14263.1. Epub 2016 Aug 24. Radiat Res. 2016. PMID: 27556353 Free PMC article.
-
Nanosensor dosimetry of mouse blood proteins after exposure to ionizing radiation.Sci Rep. 2013;3:2234. doi: 10.1038/srep02234. Sci Rep. 2013. PMID: 23868657 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Fenech M (2011) Current status, new frontiers and challenges in radiation biodosimetry using cytogenetic, transcriptomic and proteomic technologies. Radiation Measurements 46: 737–741.
-
- Pinto MM, Santos NF, Amaral A (2010) Current status of biodosimetry based on standard cytogenetic methods. Radiat Environ Biophys 49: 567–581. - PubMed
-
- Falt S, Holmberg K, Lambert B, Wennborg A (2003) Long-term global gene expression patterns in irradiated human lymphocytes. Carcinogenesis 24: 1837–1845. - PubMed
-
- Amundson SA, Do KT, Shahab S, Bittner M, Meltzer P, et al. (2000) Identification of potential mRNA biomarkers in peripheral blood lymphocytes for human exposure to ionizing radiation. Radiat Res 154: 342–346. - PubMed
-
- Turtoi A, Sharan RN, Srivastava A, Schneeweiss FH (2010) Proteomic and genomic modulations induced by gamma-irradiation of human blood lymphocytes. Int J Radiat Biol 86: 888–904. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

