Sensitive and specific immunohistochemical diagnosis of human alveolar echinococcosis with the monoclonal antibody Em2G11
- PMID: 23145198
- PMCID: PMC3493387
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0001877
Sensitive and specific immunohistochemical diagnosis of human alveolar echinococcosis with the monoclonal antibody Em2G11
Abstract
Background: Alveolar echinococcosis (AE) is caused by the metacestode stage of Echinococcus multilocularis. Differential diagnosis with cystic echinococcosis (CE) caused by E. granulosus and AE is challenging. We aimed at improving diagnosis of AE on paraffin sections of infected human tissue by immunohistochemical testing of a specific antibody.
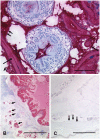
Methodology/principal findings: We have analysed 96 paraffin archived specimens, including 6 cutting needle biopsies and 3 fine needle aspirates, from patients with suspected AE or CE with the monoclonal antibody (mAb) Em2G11 specific for the Em2 antigen of E. multilocularis metacestodes. In human tissue, staining with mAb Em2G11 is highly specific for E. multilocularis metacestodes while no staining is detected in CE lesions. In addition, the antibody detects small particles of E. multilocularis (spems) of less than 1 µm outside the main lesion in necrotic tissue, liver sinusoids and lymphatic tissue most probably caused by shedding of parasitic material. The conventional histological diagnosis based on haematoxylin and eosin and PAS stainings were in accordance with the immunohistological diagnosis using mAb Em2G11 in 90 of 96 samples. In 6 samples conventional subtype diagnosis of echinococcosis had to be adjusted when revised by immunohistology with mAb Em2G11.
Conclusions/significance: Immunohistochemistry with the mAb Em2G11 is a new, highly specific and sensitive diagnostic tool for AE. The staining of small particles of E. multilocularis (spems) outside the main lesion including immunocompetent tissue, such as lymph nodes, suggests a systemic effect on the host.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures

References
-
- Eckert J, Deplazes P, Kern P (2011) Alveolar echinococcosis (Echinococcus multilocularis) and other forms of echinococcosis (Echinococcus vogeli and Echinococcus oligarthrus). In: Brown D, Palmer S, Torgerson PR, Soulsby E, editors. Zoonoses. Oxford: Oxford University Press: 671–701.
-
- Ito A, Romig T, Takahashi K (2003) Perspective on control options for Echinococcus multilocularis with particular reference to Japan. Parasitology 127: 159–72. - PubMed
-
- Marty AM, Johnson LK, Neafie RC (2000) Hydatidosis (echinococcosis). In: Meyers WM, Neafie RC, Marty AM, Wear DJ, editors. Pathology of Infectious Diseases: Volume 1, Helminthiases. Washington,D.C.: Armed Forces Institute of Pathology, American Registry of Pathology. pp145–164.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

