The putative G-protein coupled estrogen receptor agonist G-1 suppresses proliferation of ovarian and breast cancer cells in a GPER-independent manner
- PMID: 23145207
- PMCID: PMC3493027
The putative G-protein coupled estrogen receptor agonist G-1 suppresses proliferation of ovarian and breast cancer cells in a GPER-independent manner
Abstract
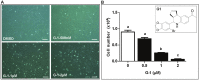
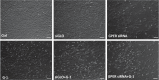
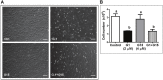
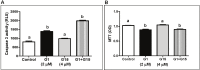
G-protein coupled estrogen receptor 1 (GPER) plays an important role in mediating estrogen action in many different tissues under both physiological and pathological conditions. G-1 (1-[4-(6-bromobenzo[1,3]dioxol-5yl)-3a,4,5,9b-tetrahydro-3H-cyclopenta [c]quinolin-8-yl]-ethanone) has been developed as a selective GPER agonist to distinguish estrogen actions mediated by GPER from those mediated by classic estrogen receptors. In the present study, we surprisingly found that G-1 suppressed proliferation and induced apoptosis of KGN cells (a human ovarian granulosa cell tumor cell line), actions that were not blocked by a selective GPER antagonist G15 or siRNA knockdown of GPER. G-1 also suppressed proliferation and induced cell apoptosis in GPER-negative HEK-293 cells and MDA-MB 231 breast cancer cells. Our results demonstrate that G-1 suppresses proliferation of ovarian and breast cancer cells in a GPER-independent manner. G-1 may be a candidate for the development of drugs against ovarian and breast cancer.
Keywords: G-1; G15; GPR30/GPER; breast cancer; estrogen receptors; ovarian cancer.
Figures


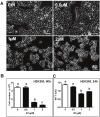

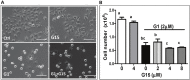
References
-
- Heldring N, Pike A, Andersson S, Matthews J, Cheng G, Hartman J, Tujague M, Ström A, Treuter E, Warner M, Gustafsson JA. Estrogen receptors: how do they signal and what are their targets. Physiological Review. 2007;87:905–931. - PubMed
-
- Thomas P, Pang Y, Filardo EJ, Dong J. Identity of an estrogen membrane receptor coupled to a G protein in human breast cancer cells. Endocrinology. 2005;146:624–632. - PubMed
-
- Filardo EJ, Quinn JA, Bland KI, Frackelton AR Jr. Estrogen-induced activation of Erk-1 and Erk-2 requires the G protein-coupled receptor homolog, GPR30, and occurs via trans-activation of the epidermal growth factor receptor through release of HB-EGF. Molecular Endocrinology. 2000;14:1649–1660. - PubMed
-
- Revankar CM, Cimino CF, Sklar LA, Arterburn JB, Prossnitz ER. A transmembrane intracellular estrogen receptor mediates rapid cell signaling. Science. 2005;307:1625–1630. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
