Efficient multicistronic co-expression of hNIS and hTPO in prostate cancer cells for nonthyroidal tumor radioiodine therapy
- PMID: 23145364
- PMCID: PMC3484425
Efficient multicistronic co-expression of hNIS and hTPO in prostate cancer cells for nonthyroidal tumor radioiodine therapy
Abstract
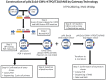
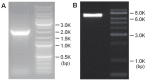
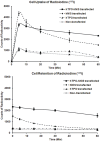
Radioiodine therapy has proven to be a safe and effective approach in the treatment of differentiated thyroid cancer. Similar treatment strategies have been exploited in nonthyroidal malignancies by transfecting hNIS gene into tumor cells or xenografts. However, rapid radioiodine efflux is often observed after radioiodine uptake, limiting the overall antitumor effects. In this study, we aimed at constructing multicistronic co-expression of hNIS and hTPO genes in tumor cells to enhance the radioiodine uptake and prolong the radioiodine retention. Driven by the cytomegalovirus promoter, hNIS and hTPO were simultaneously inserted into the expression cassette of adenoviral vector. An Ad5 viral vector (Ad-CMV-hTPO-T2A-hNIS) was assembled as a gene therapy vehicle by Gateway technology and 2A method. The co-expression of hNIS and hTPO genes was confirmed by a double-label immunofluorescence assay. The radioiodine ((125)I) uptake and efflux effects induced by co-expression of hNIS and hTPO genes were determined in transfected and non-transfected PC-3 cells. Significantly higher uptake (6.58 ± 0.56 fold, at 1 h post-incubation) and prolonged retention (5.47 ± 0.36 fold, at 1 h of cell efflux) of radioiodine ((125)I) were observed in hNIS and hTPO co-expressed PC-3 cells as compared to non-transfected PC-3 cells. We concluded that the new virus vector displayed favorable radioiodine uptake and retention properties in hNIS-hTPO transfected PC-3 cells. Our study will provide valuable information on improving the efficacy of hNIS-hTPO co-mediated radioiodine gene therapy.
Keywords: Gene therapy; gateway cloning system; hNIS; hTPO; prostate cance.
Figures






Similar articles
-
Telomerase reverse transcriptase promoter-driven expression of iodine pump genes for targeted radioiodine therapy of malignant glioma cells.Chin J Cancer. 2011 Aug;30(8):574-80. doi: 10.5732/cjc.010.10580. Chin J Cancer. 2011. PMID: 21801606 Free PMC article.
-
Cotransfected sodium iodide symporter and human tyroperoxidase genes following human telomerase reverse transcriptase promoter for targeted radioiodine therapy of malignant glioma cells.Cancer Biother Radiopharm. 2011 Aug;26(4):443-51. doi: 10.1089/cbr.2010.0908. Epub 2011 Jul 28. Cancer Biother Radiopharm. 2011. PMID: 21797672
-
[Study on the iodine 125 uptake of H460 lung cancer cell line by co-transfection with the human sodium/iodide symporter and the human thyroperoxidase].Zhongguo Fei Ai Za Zhi. 2010 Jun;13(6):575-9. doi: 10.3779/j.issn.1009-3419.2010.06.002. Zhongguo Fei Ai Za Zhi. 2010. PMID: 20681442 Free PMC article. Chinese.
-
Radioiodine therapy for castration-resistant prostate cancer following prostate-specific membrane antigen promoter-mediated transfer of the human sodium iodide symporter.Asian J Androl. 2014 Jan-Feb;16(1):120-3. doi: 10.4103/1008-682X.122354. Asian J Androl. 2014. PMID: 24369144 Free PMC article.
-
Gene therapy with sodium/iodide symporter in hepatocarcinoma.Exp Clin Endocrinol Diabetes. 2001;109(1):60-2. doi: 10.1055/s-2001-11010. Exp Clin Endocrinol Diabetes. 2001. PMID: 11573143 Review.
Cited by
-
Feasibility of using a dual-promoter recombinant baculovirus vector to coexpress EGFP and GDNF in mammalian cells.Exp Ther Med. 2014 Jun;7(6):1549-1554. doi: 10.3892/etm.2014.1655. Epub 2014 Mar 31. Exp Ther Med. 2014. PMID: 24926342 Free PMC article.
-
BMP-2 overexpression augments vascular smooth muscle cell motility by upregulating myosin Va via Erk signaling.Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2014;2014:294150. doi: 10.1155/2014/294150. Epub 2014 Mar 20. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2014. PMID: 24790701 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Nilsson M. Molecular and cellular mechanisms of transepithelial iodide transport in the thyroid. Biofactors. 1999;10:277–85. - PubMed
-
- Trapasso F, Iuliano R, Chiefari E, Arturi F, Stella A, Filetti S, Fusco A, Russo D. Iodide symporter gene expression in normal and transformed rat thyroid cells. Eur J Endocrinol. 1999;140:447–51. - PubMed
-
- Filetti S, Bidart JM, Arturi F, Caillou B, Russo D, Schlumberger M. Sodium/iodide symporter: a key transport system in thyroid cancer cell metabolism. Eur J Endocrinol. 1999;141:443–57. - PubMed
-
- Lazar V, Bidart JM, Caillou B, Mahe C, Lacroix L, Filetti S, Schlumberger M. Expression of the Na+/I- symporter gene in human thyroid tumors: a comparison study with other thyroidspecific genes. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1999;84:3228–34. - PubMed
-
- Reiners C, Farahati J. 131I therapy of thyroid cancer patients. Q J Nucl Med. 1999;43:324–35. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
