Effect of laparoscopic splenectomy in patients with Hepatitis C and cirrhosis carrying IL28B minor genotype
- PMID: 23145809
- PMCID: PMC3503804
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-230X-12-158
Effect of laparoscopic splenectomy in patients with Hepatitis C and cirrhosis carrying IL28B minor genotype
Abstract
Background: IL28B and ITPA genetic variants are associated with the outcome of pegylated-interferon and ribavirin (PEG-IFN/RBV) therapy. However, the significance of these genetic variants in cirrhotic patients following splenectomy has not been determined.
Methods: Thirty-seven patients with HCV-induced cirrhosis who underwent laparoscopic splenectomy (Spx group) and 90 who did not (non-Spx group) were genotyped for IL28B and ITPA. The outcome or adverse effects were compared in each group. Interferon-stimulated gene 15 (ISG15) and protein kinase R expression in the spleen was measured using total RNA extracted from exenterate spleen.
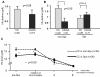
Results: Sustained virological response (SVR) rate was higher in patients carrying IL28B major genotype following splenectomy (50% vs 27.3%) and in patients carrying minor genotype in the Spx group compared to non-Spx group (27.3% vs 3.6%, P < 0.05). Pretreatment splenic ISG expression was higher in patients carrying IL28B major. There was no difference in progression of anemia or thrombocytopenia between patients carrying each ITPA genotype in the Spx group. Although splenectomy did not increase hemoglobin (Hb) level, Hb decline tended to be greater in the non-Spx group. In contrast, splenectomy significantly increased platelet count (61.1 × 103/μl vs 168.7 × 103/μl, P < 0.01), which was maintained during the course of PEG-IFN/RBV therapy.
Conclusions: IL28B genetic variants correlated with response to PEG-IFN/RBV following splenectomy. Splenectomy improved SVR rate among patients carrying IL28B minor genotype and protected against anemia and thrombocytopenia during the course of PEG-IFN/RBV therapy regardless of ITPA genotype.
Figures


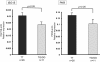
Similar articles
-
Thrombocytopenia in pegylated interferon and ribavirin combination therapy for chronic hepatitis C.J Gastroenterol. 2014 Aug;49(8):1253-63. doi: 10.1007/s00535-013-0884-0. Epub 2013 Sep 25. J Gastroenterol. 2014. PMID: 24065124 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
IL28B polymorphism as a predictor of antiviral response in chronic hepatitis C.World J Gastroenterol. 2012 Sep 21;18(35):4892-7. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v18.i35.4892. World J Gastroenterol. 2012. PMID: 23002361 Free PMC article.
-
Lead-in treatment with interferon-β/ribavirin may modify the early hepatitis C virus dynamics in pegylated interferon alpha-2b/ribavirin combination for chronic hepatitis C patients with the IL28B minor genotype.J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2013 Mar;28(3):443-9. doi: 10.1111/jgh.12039. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2013. PMID: 23173698 Clinical Trial.
-
Review article: genetic factors that modify the outcome of viral hepatitis.Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2014 May;39(10):1059-70. doi: 10.1111/apt.12717. Epub 2014 Mar 24. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2014. PMID: 24654629 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Host genetics.Curr Opin HIV AIDS. 2011 Nov;6(6):491-500. doi: 10.1097/COH.0b013e32834bca2d. Curr Opin HIV AIDS. 2011. PMID: 21918436 Review.
Cited by
-
Laparoscopic splenectomy for hypersplenism secondary to liver cirrhosis and portal hypertension.World J Gastroenterol. 2014 May 21;20(19):5794-800. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i19.5794. World J Gastroenterol. 2014. PMID: 24914339 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Strategies to treat interferon-induced graft dysfunction after living donor liver transplantation for hepatitis C.Hepatol Int. 2014 Apr;8(2):285-92. doi: 10.1007/s12072-013-9496-2. Epub 2013 Dec 27. Hepatol Int. 2014. PMID: 26202510
-
Effect of spleen operation on antiviral treatment in hepatitis C virus-related cirrhotic patients.World J Gastroenterol. 2014 Nov 7;20(41):15387-97. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i41.15387. World J Gastroenterol. 2014. PMID: 25386089 Free PMC article.
-
Prior Esophagogastric Devascularization Followed by Splenectomy for Liver Cirrhosis with Portal Hypertension: A Modified Laparoscopic Technique.Gastroenterol Res Pract. 2019 Feb 3;2019:2623749. doi: 10.1155/2019/2623749. eCollection 2019. Gastroenterol Res Pract. 2019. PMID: 30863438 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Global Burden of Hepatitis C Working Group. Global burden of disease (GBD) for hepatitis C. J Clin Pharmacol. 2004;44:20–29. - PubMed
-
- Hadziyannis SJ, Sette H Jr, Morgan TR, Balan V, Diago M, Marcellin P. et al.Peginterferon-alpha2a and ribavirin combination therapy in chronic hepatitis C: a randomized study of treatment duration and ribavirin dose. Ann Intern Med. 2004;140(5):346–355. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

