DNA damage induces nucleoid compaction via the Mre11-Rad50 complex in the archaeon Haloferax volcanii
- PMID: 23145964
- PMCID: PMC3565448
- DOI: 10.1111/mmi.12091
DNA damage induces nucleoid compaction via the Mre11-Rad50 complex in the archaeon Haloferax volcanii
Abstract
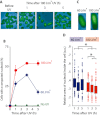
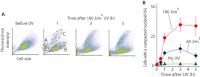
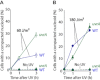
In prokaryotes the genome is organized in a dynamic structure called the nucleoid, which is embedded in the cytoplasm. We show here that in the archaeon Haloferax volcanii, compaction and reorganization of the nucleoid is induced by stresses that damage the genome or interfere with its replication. The fraction of cells exhibiting nucleoid compaction was proportional to the dose of the DNA damaging agent, and results obtained in cells defective for nucleotide excision repair suggest that breakage of DNA strands triggers reorganization of the nucleoid. We observed that compaction depends on the Mre11-Rad50 complex, suggesting a link to DNA double-strand break repair. However, compaction was observed in a radA mutant, indicating that the role of Mre11-Rad50 in nucleoid reorganisation is independent of homologous recombination. We therefore propose that nucleoid compaction is part of a DNA damage response that accelerates cell recovery by helping DNA repair proteins to locate their targets, and facilitating the search for intact DNA sequences during homologous recombination.
© 2012 Blackwell Publishing Ltd.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Mre11-Rad50 promotes rapid repair of DNA damage in the polyploid archaeon Haloferax volcanii by restraining homologous recombination.PLoS Genet. 2009 Jul;5(7):e1000552. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1000552. Epub 2009 Jul 10. PLoS Genet. 2009. PMID: 19593371 Free PMC article.
-
Rad50 is not essential for the Mre11-dependent repair of DNA double-strand breaks in Halobacterium sp. strain NRC-1.J Bacteriol. 2008 Aug;190(15):5210-6. doi: 10.1128/JB.00292-08. Epub 2008 May 23. J Bacteriol. 2008. PMID: 18502851 Free PMC article.
-
The P. furiosus mre11/rad50 complex promotes 5' strand resection at a DNA double-strand break.Cell. 2008 Oct 17;135(2):250-60. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2008.09.054. Cell. 2008. PMID: 18957200 Free PMC article.
-
Haloferax volcanii-a model archaeon for studying DNA replication and repair.Open Biol. 2020 Dec;10(12):200293. doi: 10.1098/rsob.200293. Epub 2020 Dec 2. Open Biol. 2020. PMID: 33259746 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Turning the Mre11/Rad50 DNA repair complex on its head: lessons from SMC protein hinges, dynamic coiled-coil movements and DNA loop-extrusion?Biochem Soc Trans. 2020 Dec 18;48(6):2359-2376. doi: 10.1042/BST20170168. Biochem Soc Trans. 2020. PMID: 33300987 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Cas1 and Fen1 Display Equivalent Functions During Archaeal DNA Repair.Front Microbiol. 2022 Apr 15;13:822304. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2022.822304. eCollection 2022. Front Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 35495653 Free PMC article.
-
Structural studies of DNA end detection and resection in homologous recombination.Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2014 Jul 31;6(10):a017962. doi: 10.1101/cshperspect.a017962. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2014. PMID: 25081516 Free PMC article. Review.
-
PCNA-binding proteins in the archaea: novel functionality beyond the conserved core.Curr Genet. 2016 Aug;62(3):527-32. doi: 10.1007/s00294-016-0577-3. Epub 2016 Feb 17. Curr Genet. 2016. PMID: 26886233 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Chromosome architecture in an archaeal species naturally lacking structural maintenance of chromosomes proteins.Nat Microbiol. 2024 Jan;9(1):263-273. doi: 10.1038/s41564-023-01540-6. Epub 2023 Dec 18. Nat Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 38110698 Free PMC article.
-
Stress-induced condensation of bacterial genomes results in re-pairing of sister chromosomes: implications for double strand DNA break repair.J Biol Chem. 2013 Aug 30;288(35):25659-25667. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M113.473025. Epub 2013 Jul 24. J Biol Chem. 2013. PMID: 23884460 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Allers T, Mevarech M. Archaeal genetics – the third way. Nat Rev Genet. 2005;6:58–73. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

