Diastolic timed Vibro-Percussion at 50 Hz delivered across a chest wall sized meat barrier enhances clot dissolution and remotely administered Streptokinase effectiveness in an in-vitro model of acute coronary thrombosis
- PMID: 23146079
- PMCID: PMC3534480
- DOI: 10.1186/1477-9560-10-23
Diastolic timed Vibro-Percussion at 50 Hz delivered across a chest wall sized meat barrier enhances clot dissolution and remotely administered Streptokinase effectiveness in an in-vitro model of acute coronary thrombosis
Abstract
Background: Low Frequency Vibro-Percussion (LFVP) assists clearance of thrombi in catheter systems and when applied to the heart and timed to diastole is known to enhance coronary flow. However LFVP on a clotted coronary like vessel given engagement over a chest wall sized barrier (to resemble non-invasive heart attack therapy) requires study.
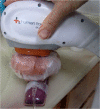
Methods: One hour old clots (n=16) were dispensed within a flexible segment of Soft-Flo catheter (4 mm lumen), weighted, interfaced with Heparinized Saline (HS), secured atop a curved dampening base, and photographed. A ~4 cm meat slab was placed over the segment and randomized to receive intermittent LFVP (engaged, - disengaged at 1 second intervals), or no LFVP for 20 minutes. HS was pulsed (~120/80 mmHg), with the diastolic phase coordinated to match LFVP delivery. The segment was then re-photographed and aspirated of fluid to determine post clot weight. The trial was then repeated with 0.5 mls of Streptokinase (15,000 IU/100 microlitre) delivered ~ 2 cm upstream from the clot.
Results: LFVP - HS only samples (vs. controls) showed; a) development of clot length fluid channels absent in the control group (p < 0.0002); b) enhanced dissolved clot mixing scores ( 5.0 vs. 0.8, p < 2.8 E - 6); and c) increased percent clot dissolution (23.0% vs. 1.8% respectively, p < 8.5 E-6). LFVP - SK samples had a similar comparative clot disruptive profile, however fluid channels developed faster and percent clot dissolution more than doubled (51.0% vs. 3.0%, p< 9.8 E- 6).
Conclusion: Diastolic timed LFVP (50 Hz) engaged across a chest wall sized barrier enhances clot disruptive effects to an underlying coronary like system.
Figures










References
-
- Jacobs AK, Antman EM, Ellrodt G. The American Heart Association’s Acute Myocardial Infarction (AMI) Advisory Working Group et al.Recommendation to develop strategies to increase the number of ST-segment-elevation myocardial infarction patients with timely access to primary percutaneous coronary intervention. Circulation. 2006;113:2152–2163. 10.161?CIRCULATIONAHA.106.174477. - PubMed
-
- Van de Werf F, Ardissino D, Betriu A, Cokkinos DV, Falk E, Fox KA, Julian D, Lengyel M, Neumann FJ, Ruzyllo W, Thygesen C, Underwood SR, Vahanian A, Verheugt FWA, Wijns W. Management of acute myocardial infarction in patients presenting with ST-segment elevation. The task force on the management of acute myocardial infarction of the European Society of Cardiology. Eur Heart J. 2003;24:28–66. doi: 10.1016/50195-668x(02)00618-8. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

