Size-dependent antimicrobial properties of sugar-encapsulated gold nanoparticles synthesized by a green method
- PMID: 23146145
- PMCID: PMC3533927
- DOI: 10.1186/1556-276X-7-623
Size-dependent antimicrobial properties of sugar-encapsulated gold nanoparticles synthesized by a green method
Abstract
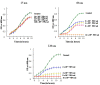
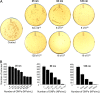
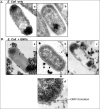
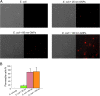
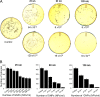
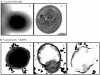
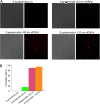
The antimicrobial properties of dextrose-encapsulated gold nanoparticles (dGNPs) with average diameters of 25, 60, and 120 nm (± 5) and synthesized by green chemistry principles were investigated against both Gram-negative and Gram-positive bacteria. Studies were performed involving the effect of dGNPs on the growth, morphology, and ultrastructural properties of bacteria. dGNPs were found to have significant dose-dependent antibacterial activity which was also proportional to their size. Experiments revealed the dGNPs to be bacteriostatic as well as bactericidal. The dGNPs exhibited their bactericidal action by disrupting the bacterial cell membrane which leads to the leakage of cytoplasmic content. The overall outcome of this study suggests that green-synthesized dGNPs hold promise as a potent antibacterial agent against a wide range of disease-causing bacteria by preventing and controlling possible infections or diseases.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Activating the Antibacterial Effect of 4,6-Diamino-2-pyrimidinethiol-Modified Gold Nanoparticles by Reducing their Sizes.Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2020 Dec 21;59(52):23471-23475. doi: 10.1002/anie.202008584. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2020. PMID: 32886827
-
Selective cytotoxicity of green synthesized silver nanoparticles against the MCF-7 tumor cell line and their enhanced antioxidant and antimicrobial properties.Int J Nanomedicine. 2018 Nov 27;13:8013-8024. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S189295. eCollection 2018. Int J Nanomedicine. 2018. PMID: 30568442 Free PMC article.
-
Size-dependent antimicrobial properties of CuO nanoparticles against Gram-positive and -negative bacterial strains.Int J Nanomedicine. 2012;7:3527-35. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S29020. Epub 2012 Jul 10. Int J Nanomedicine. 2012. PMID: 22848176 Free PMC article.
-
Spotlight on therapeutic efficiency of green synthesis metals and their oxide nanoparticles in periodontitis.J Nanobiotechnology. 2024 Jan 5;22(1):21. doi: 10.1186/s12951-023-02284-5. J Nanobiotechnology. 2024. PMID: 38183090 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Natural Products-Based Metallic Nanoparticles as Antimicrobial Agents.Front Pharmacol. 2022 Jun 2;13:895616. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.895616. eCollection 2022. Front Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 35721199 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Cytotoxicity and antibacterial activity of gold-supported cerium oxide nanoparticles.Int J Nanomedicine. 2014 Nov 27;9:5515-31. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S70087. eCollection 2014. Int J Nanomedicine. 2014. PMID: 25473288 Free PMC article.
-
Size-dependent gold nanoparticles induce macrophage M2 polarization and promote intracellular clearance of Staphylococcus aureus to alleviate tissue infection.Mater Today Bio. 2023 Jun 20;21:100700. doi: 10.1016/j.mtbio.2023.100700. eCollection 2023 Aug. Mater Today Bio. 2023. PMID: 37455821 Free PMC article.
-
Gold Nanoparticles: Can They Be the Next Magic Bullet for Multidrug-Resistant Bacteria?Nanomaterials (Basel). 2021 Jan 26;11(2):312. doi: 10.3390/nano11020312. Nanomaterials (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33530434 Free PMC article. Review.
-
XAV939: from a small inhibitor to a potent drug bioconjugate when delivered by gold nanoparticles.Bioconjug Chem. 2014 Feb 19;25(2):207-215. doi: 10.1021/bc400271x. Epub 2014 Jan 10. Bioconjug Chem. 2014. PMID: 24409808 Free PMC article.
-
Development of noncytotoxic chitosan-gold nanocomposites as efficient antibacterial materials.ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2015 Jan 21;7(2):1087-99. doi: 10.1021/am508094e. Epub 2015 Jan 8. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2015. PMID: 25522372 Free PMC article.
References
-
- So AD, Gupta N, Brahmachari SK, Chopra I, Munos B, Nathan C, Outterson K, Paccaud JP, Payne DJ, Peeling RW, Spigelman M, Weigelt J. Towards new business models for R&D for novel antibiotics. Drug Resist Update. 2011;14:89–94. - PubMed
-
- Balland O, Pinto-Alphandary H, Viron A, Puvion E, Andremont A, Couvreur P. Intracellular distribution of ampicillin in murine macrophages infected with Salmonella typhimurium and treated with (3H) ampicillin-loaded nanoparticles. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1996;37:105–115. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

