A fluorogenic phospholipid for the detection of lysosomal phospholipase A2 activity
- PMID: 23146589
- PMCID: PMC3557754
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ab.2012.11.004
A fluorogenic phospholipid for the detection of lysosomal phospholipase A2 activity
Abstract
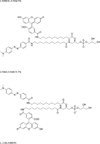
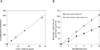
Lysosomal phospholipase A2 (group XV PLA2, LPLA2) is a lysosomal enzyme linked to drug-induced phospholipidosis. We developed phospholipid "smart probes" based on the conversion of a quenched fluorogenic substrate to a fluorescent product. Due to the preference of LPLA2 for phosphatidylglycerol, three fluorogenic phosphatidylglycerols were synthesized. Two fluorogenic phosphatidylglycerols were conjugated with one FAM (fluorescein amidite) group and one DABCYL [4-(4-dimethylaminophenylazo)-benzoyl] group; the third substrate consisted of two FAM groups conjugated at the sn-1 and sn-2 positions. The sn-1 ester linkage was replaced with an amide linkage. 1-FAM-2-DABCYL-PG was degraded by recombinant LPLA2 and mouse serum but not by the serum obtained from LPLA2-deficient mice when 1,2-dioleoyl-PG/1-FAM-2-DABCYL-PG liposomes were used. The formation of 1-FAM-lyso-PG generated from 1-FAM-2-DABCYL-PG in the presence of LPLA2 was quantitatively determined by fluorescent measurements. The 1-FAM-2-DABCYL-PG incorporated into 1,2-dioleoyl-phosphatidylcholine/sulfatide liposomes was used to evaluate the effect of the cationic amphiphilic drugs amiodarone and fluoxetine on LPLA2 activity. The IC(50) values of amiodarone and fluoxetine estimated by fluorescent measurement were 10 and 19μM, respectively. These results indicate that 1-FAM-2-DABCYL-PG is a specific substrate for LPLA2 and a useful reagent for the detection of LPLA2 activity from multiple sources.
Published by Elsevier Inc.
Figures




References
-
- Abe A, Hiraoka M, Wild S, Wilcoxen SE, Paine R, 3rd, Shayman JA. Lysosomal phospholipase A2 is selectively expressed in alveolar macrophages. J Biol Chem. 2004;279:42605–42611. - PubMed
-
- Abe A, Hiraoka M, Shayman JA. A role for lysosomal phospholipase A2 in drug induced phospholipidosis. Drug Metab Lett. 2007;1:49–53. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

