Leptin and insulin pathways in POMC and AgRP neurons that modulate energy balance and glucose homeostasis
- PMID: 23146889
- PMCID: PMC3512417
- DOI: 10.1038/embor.2012.174
Leptin and insulin pathways in POMC and AgRP neurons that modulate energy balance and glucose homeostasis
Abstract
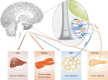
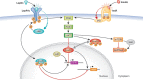
With the steady rise in the prevalence of obesity and its associated diseases, research aimed at understanding the mechanisms that regulate and control whole body energy homeostasis has gained new interest. Leptin and insulin, two anorectic hormones, have key roles in the regulation of body weight and energy homeostasis, as highlighted by the fact that several obese patients develop resistance to these hormones. Within the brain, the hypothalamic proopiomelanocortin and agouti-related protein neurons have been identified as major targets of leptin and insulin action. Many studies have attempted to discern the individual contributions of various components of the principal pathways that mediate the central effects of leptin and insulin. The aim of this review is to discuss the latest findings that might shed light on, and lead to a better understanding of, energy balance and glucose homeostasis. In addition, recently discovered targets and mechanisms that mediate hormonal action in the brain are highlighted.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Wang Y et al. (2008) Will all Americans become overweight or obese? Estimating the progression and cost of the US obesity epidemic. Obesity (Silver Spring) 16: 2323–2330 - PubMed
-
- Wang YC et al. (2011) Health and economic burden of the projected obesity trends in the USA and the UK. Lancet 378: 815–825 - PubMed
-
- Woods SC, Seeley RJ (2000) Adiposity signals and the control of energy homeostasis. Nutrition 16: 894–902 - PubMed
-
- Mohr B (1840) Hypertrophie der hipófisis cerebral und druck adurch bedingter auf die hirngrundflache, complementos besondere auf die sehnerven, das quiasma derselben und den linkseitigen hirnschinkel. Wschr des Heilk 6: 565–571
-
- Frohlich A (1901) Ein fall von tumor der hypophysis cerebri ohne akromegalie wien klin. Rundschau 15: 883–906
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

