Lamins in development, tissue maintenance and stress
- PMID: 23146893
- PMCID: PMC3512410
- DOI: 10.1038/embor.2012.167
Lamins in development, tissue maintenance and stress
Abstract
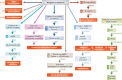
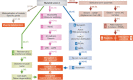
Lamins are nuclear intermediate filament proteins. They provide mechanical stability, organize chromatin and regulate transcription, replication, nuclear assembly and nuclear positioning. Recent studies provide new insights into the role of lamins in development, differentiation and tissue response to mechanical, reactive oxygen species and thermal stresses. These studies also propose the existence of separate filament networks for A- and B-type lamins and identify new roles for the different networks. Furthermore, they show changes in lamin composition in different cell types, propose explanations for the more than 14 distinct human diseases caused by lamin A and lamin C mutations and propose a role for lamin B1 in these diseases.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures





References
-
- Stuurman N, Heins S, Aebi U (1998) Nuclear lamins: their structure, assembly, and interactions. J Struct Biol 122: 42–66 - PubMed
-
- Aebi U, Cohn J, Buhle L, Gerace L (1986) The nuclear lamina is a meshwork of intermediate-type filaments. Nature 323: 560–564 - PubMed
-
- Goldberg MW, Huttenlauch I, Hutchison CJ, Stick R (2008) Filaments made from A- and B-type lamins differ in structure and organization. J Cell Sci 121: 215–225 - PubMed
-
- Ben-Harush K, Wiesel N, Frenkiel-Krispin D, Moeller D, Soreq E, Aebi U, Herrmann H, Gruenbaum Y, Medalia O (2009) The supramolecular organization of the C. elegans nuclear lamin filament. J Mol Biol 386: 1392–1402 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

