Optogenetic and potassium channel gene therapy in a rodent model of focal neocortical epilepsy
- PMID: 23147003
- PMCID: PMC3605784
- DOI: 10.1126/scitranslmed.3004190
Optogenetic and potassium channel gene therapy in a rodent model of focal neocortical epilepsy
Abstract
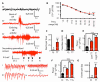
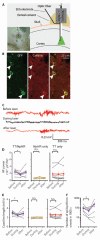
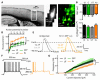
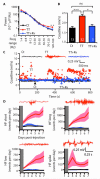
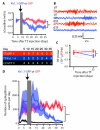
Neocortical epilepsy is frequently drug-resistant. Surgery to remove the epileptogenic zone is only feasible in a minority of cases, leaving many patients without an effective treatment. We report the potential efficacy of gene therapy in focal neocortical epilepsy using a rodent model in which epilepsy is induced by tetanus toxin injection in the motor cortex. By applying several complementary methods that use continuous wireless electroencephalographic monitoring to quantify epileptic activity, we observed increases in high frequency activity and in the occurrence of epileptiform events. Pyramidal neurons in the epileptic focus showed enhanced intrinsic excitability consistent with seizure generation. Optogenetic inhibition of a subset of principal neurons transduced with halorhodopsin targeted to the epileptic focus by lentiviral delivery was sufficient to attenuate electroencephalographic seizures. Local lentiviral overexpression of the potassium channel Kv1.1 reduced the intrinsic excitability of transduced pyramidal neurons. Coinjection of this Kv1.1 lentivirus with tetanus toxin fully prevented the occurrence of electroencephalographic seizures. Finally, administration of the Kv1.1 lentivirus to an established epileptic focus progressively suppressed epileptic activity over several weeks without detectable behavioral side effects. Thus, gene therapy in a rodent model can be used to suppress seizures acutely, prevent their occurrence after an epileptogenic stimulus, and successfully treat established focal epilepsy.
Figures
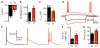
Comment in
-
Treating epilepsy with a light potassium diet.Sci Transl Med. 2012 Nov 21;4(161):161fs40. doi: 10.1126/scitranslmed.3005297. Sci Transl Med. 2012. PMID: 23175707
-
Epilepsy: shining a light on seizure control-optogenetic approach shows promise for treatment and prevention of epilepsies.Nat Rev Neurol. 2013 Jan;9(1):1. doi: 10.1038/nrneurol.2012.256. Epub 2012 Dec 11. Nat Rev Neurol. 2013. PMID: 23229406 No abstract available.
-
Gene therapy: suppressing seizures.Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2013 Jan;12(1):22. doi: 10.1038/nrd3918. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2013. PMID: 23274464 No abstract available.
References
-
- Kwan P, Schachter SC, Brodie MJ. Drug-resistant epilepsy. N. Engl. J. Med. 2011;365:919–926. - PubMed
-
- Annegers JF, Hauser WA, Elveback LR. Remission of seizures and relapse in patients with epilepsy. Epilepsia. 1979;20:729–737. - PubMed
-
- Jasper’s Basic Mechanisms of the Epilepsies—NCBI Bookshelf. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK50785/
-
- Rosenow F, Lüders H. Presurgical evaluation of epilepsy. Brain. 2001;124:1683–1700. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

