Heart-brain signaling in patent foramen ovale-related stroke: differential plasma proteomic expression patterns revealed with a 2-pass liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry discovery workflow
- PMID: 23147404
- PMCID: PMC3668452
- DOI: 10.2310/JIM.0b013e318276de0e
Heart-brain signaling in patent foramen ovale-related stroke: differential plasma proteomic expression patterns revealed with a 2-pass liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry discovery workflow
Abstract
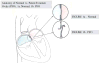
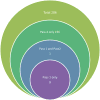
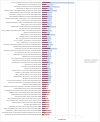
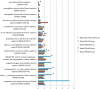
Patent foramen ovale (PFO) is highly prevalent and associated with more than 150,000 strokes per year. Traditionally, it is thought that PFOs facilitate strokes by allowing venous clots to travel directly to the brain. However, only a small portion of PFO stroke patients have a known tendency to form blood clots, and the optimal treatment for this multiorgan disease is unclear. Therefore, mapping the changes in systemic circulation of PFO-related stroke is crucial in understanding the pathophysiology to individualize the best clinical treatment for each patient. We initiated a study using a novel quantitative, 2-pass discovery workflow using high-resolution liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry/mass spectrometry coupled with label-free analysis to track protein expression in PFO patients before and after endovascular closure of the PFO. Using this approach, we were able to demonstrate quantitative differences in protein expression between both PFO-related and non-PFO-related ischemic stroke groups as well as before and after PFO closure. As an initial step in understanding the molecular landscape of PFO-related physiology, our methods have yielded biologically relevant information on the synergistic and functional redundancy of various cell-signaling molecules with respect to PFO circulatory physiology. The resulting protein expression patterns were related to canonical pathways including prothrombin activation, atherosclerosis signaling, acute-phase response, LXR/RXR activation, and coagulation system. In particular, after PFO closure, numerous proteins demonstrated reduced expression in stroke-related canonical pathways such as acute inflammatory response and coagulation signaling. These findings demonstrate the feasibility and robustness of using a proteomic approach for biomarker discovery to help gauge therapeutic efficacy in stroke.
Figures



References
-
- Calvert PA, Rana BS, Kydd AC, Shapiro LM. Patent foramen ovale: anatomy, outcomes, and closure. Nat Rev Cardiol. 2011;8:148–160. - PubMed
-
- Kunitz SC, Gross CR, Heyman A, Kase CS, Mohr JP, Price TR, Wolf PA. The pilot Stroke Data Bank: definition, design, and data. Stroke. 1984;15:740–746. - PubMed
-
- Foulkes MA, Wolf PA, Price TR, Mohr JP, Hier DB. The Stroke Data Bank: design, methods, and baseline characteristics. Stroke. 1988;19:547–554. - PubMed
-
- Sacco RL, Ellenberg JH, Mohr JP, Tatemichi TK, Hier DB, Price TR, Wolf PA. Infarcts of undetermined cause: the NINCDS Stroke Data Bank. Ann Neurol. 1989;25:382–390. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

