Clinical guideline: management of gastroparesis
- PMID: 23147521
- PMCID: PMC3722580
- DOI: 10.1038/ajg.2012.373
Clinical guideline: management of gastroparesis
Abstract
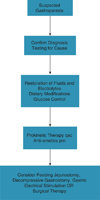
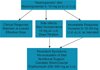
This guideline presents recommendations for the evaluation and management of patients with gastroparesis. Gastroparesis is identified in clinical practice through the recognition of the clinical symptoms and documentation of delayed gastric emptying. Symptoms from gastroparesis include nausea, vomiting, early satiety, postprandial fullness, bloating, and upper abdominal pain. Management of gastroparesis should include assessment and correction of nutritional state, relief of symptoms, improvement of gastric emptying and, in diabetics, glycemic control. Patient nutritional state should be managed by oral dietary modifications. If oral intake is not adequate, then enteral nutrition via jejunostomy tube needs to be considered. Parenteral nutrition is rarely required when hydration and nutritional state cannot be maintained. Medical treatment entails use of prokinetic and antiemetic therapies. Current approved treatment options, including metoclopramide and gastric electrical stimulation (GES, approved on a humanitarian device exemption), do not adequately address clinical need. Antiemetics have not been specifically tested in gastroparesis, but they may relieve nausea and vomiting. Other medications aimed at symptom relief include unapproved medications or off-label indications, and include domperidone, erythromycin (primarily over a short term), and centrally acting antidepressants used as symptom modulators. GES may relieve symptoms, including weekly vomiting frequency, and the need for nutritional supplementation, based on open-label studies. Second-line approaches include venting gastrostomy or feeding jejunostomy; intrapyloric botulinum toxin injection was not effective in randomized controlled trials. Most of these treatments are based on open-label treatment trials and small numbers. Partial gastrectomy and pyloroplasty should be used rarely, only in carefully selected patients. Attention should be given to the development of new effective therapies for symptomatic control.
Figures
Comment in
-
Update on clinical guidelines for the management of gastroparesis.Am J Gastroenterol. 2013 Sep;108(9):1538-9. doi: 10.1038/ajg.2013.212. Am J Gastroenterol. 2013. PMID: 24005360 No abstract available.
-
Response to Arnold and Beaves.Am J Gastroenterol. 2013 Sep;108(9):1539-40. doi: 10.1038/ajg.2013.215. Am J Gastroenterol. 2013. PMID: 24005361 No abstract available.
References
-
- Tack J, Bisschops R, Sarnelli G. Pathophysiology and treatment of functional dyspepsia. Gastroenterology. 2004;127:1239–1255. - PubMed
-
- Sarnelli G, Caenepeel P, Geypens B, et al. Symptoms associated with impaired gastric emptying of solids and liquids in functional dyspepsia. Am J Gastroenterol. 2003;98:783–788. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical