The association of a La module with the PABP-interacting motif PAM2 is a recurrent evolutionary process that led to the neofunctionalization of La-related proteins
- PMID: 23148093
- PMCID: PMC3527725
- DOI: 10.1261/rna.035469.112
The association of a La module with the PABP-interacting motif PAM2 is a recurrent evolutionary process that led to the neofunctionalization of La-related proteins
Abstract
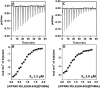
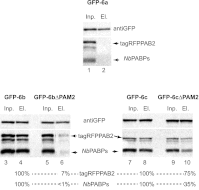
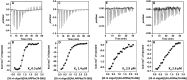
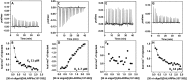
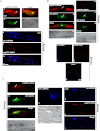
La-related proteins (LARPs) are largely uncharacterized factors, well conserved throughout evolution. Recent reports on the function of human LARP4 and LARP6 suggest that these proteins fulfill key functions in mRNA metabolism and/or translation. We report here a detailed evolutionary history of the LARP4 and 6 families in eukaryotes. Genes coding for LARP4 and 6 were duplicated in the common ancestor of the vertebrate lineage, but one LARP6 gene was subsequently lost in the common ancestor of the eutherian lineage. The LARP6 gene was also independently duplicated several times in the vascular plant lineage. We observed that vertebrate LARP4 and plant LARP6 duplication events were correlated with the acquisition of a PABP-interacting motif 2 (PAM2) and with a significant reorganization of their RNA-binding modules. Using isothermal titration calorimetry (ITC) and immunoprecipitation methods, we show that the two plant PAM2-containing LARP6s (LARP6b and c) can, indeed, interact with the major plant poly(A)-binding protein (PAB2), while the third plant LARP6 (LARP6a) is unable to do so. We also analyzed the RNA-binding properties and the subcellular localizations of the two types of plant LARP6 proteins and found that they display nonredundant characteristics. As a whole, our results support a model in which the acquisition by LARP4 and LARP6 of a PAM2 allowed their targeting to mRNA 3' UTRs and led to their neofunctionalization.
Figures


Similar articles
-
La-related protein 4 binds poly(A), interacts with the poly(A)-binding protein MLLE domain via a variant PAM2w motif, and can promote mRNA stability.Mol Cell Biol. 2011 Feb;31(3):542-56. doi: 10.1128/MCB.01162-10. Epub 2010 Nov 22. Mol Cell Biol. 2011. PMID: 21098120 Free PMC article.
-
The isolated La-module of LARP1 mediates 3' poly(A) protection and mRNA stabilization, dependent on its intrinsic PAM2 binding to PABPC1.RNA Biol. 2021 Feb;18(2):275-289. doi: 10.1080/15476286.2020.1860376. Epub 2020 Dec 23. RNA Biol. 2021. PMID: 33292040 Free PMC article.
-
LARP1 and LARP4: up close with PABP for mRNA 3' poly(A) protection and stabilization.RNA Biol. 2021 Feb;18(2):259-274. doi: 10.1080/15476286.2020.1868753. Epub 2021 Jan 31. RNA Biol. 2021. PMID: 33522422 Free PMC article. Review.
-
LARP4A recognizes polyA RNA via a novel binding mechanism mediated by disordered regions and involving the PAM2w motif, revealing interplay between PABP, LARP4A and mRNA.Nucleic Acids Res. 2019 May 7;47(8):4272-4291. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkz144. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019. PMID: 30820564 Free PMC article.
-
LARP6 proteins in plants.Biochem Soc Trans. 2021 Nov 1;49(5):1975-1983. doi: 10.1042/BST20200715. Biochem Soc Trans. 2021. PMID: 34709399 Review.
Cited by
-
A Maize Male Gametophyte-Specific Gene Encodes ZmLARP6c1, a Potential RNA-Binding Protein Required for Competitive Pollen Tube Growth.Front Plant Sci. 2021 Feb 25;12:635244. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2021.635244. eCollection 2021. Front Plant Sci. 2021. PMID: 33719310 Free PMC article.
-
La-related Protein 1 (LARP1) Represses Terminal Oligopyrimidine (TOP) mRNA Translation Downstream of mTOR Complex 1 (mTORC1).J Biol Chem. 2015 Jun 26;290(26):15996-6020. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M114.621730. Epub 2015 May 4. J Biol Chem. 2015. PMID: 25940091 Free PMC article.
-
TOP mRNPs: Molecular Mechanisms and Principles of Regulation.Biomolecules. 2020 Jun 27;10(7):969. doi: 10.3390/biom10070969. Biomolecules. 2020. PMID: 32605040 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Human La binds mRNAs through contacts to the poly(A) tail.Nucleic Acids Res. 2018 May 4;46(8):4228-4240. doi: 10.1093/nar/gky090. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018. PMID: 29447394 Free PMC article.
-
The LARP6 La module from Tetrabaena socialis reveals structural and functional differences from plant and animal LARP6 homologues.RNA Biol. 2025 Dec;22(1):1-9. doi: 10.1080/15476286.2025.2489303. Epub 2025 Apr 9. RNA Biol. 2025. PMID: 40181506 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Anderson P, Kedersha N 2009. RNA granules: Post-transcriptional and epigenetic modulators of gene expression. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 10: 430–436 - PubMed
-
- Anisimova M, Gascuel O 2006. Approximate likelihood-ratio test for branches: A fast, accurate, and powerful alternative. Syst Biol 55: 539–552 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
